Inhibition of PDGF-BB by Factor VII-activating protease (FSAP) is neutralized by protease nexin-1, and the FSAP-inhibitor complexes are internalized via LRP
- PMID: 17298300
- PMCID: PMC1868796
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20061630
Inhibition of PDGF-BB by Factor VII-activating protease (FSAP) is neutralized by protease nexin-1, and the FSAP-inhibitor complexes are internalized via LRP
Abstract
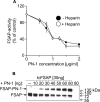
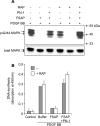
FSAP (Factor VII-activating protease) can inhibit neointima formation and VSMC (vascular smooth-muscle cell) proliferation by cleavage of PDGF-BB (platelet-derived growth factor-BB). Negatively charged polyanions lead to autoactivation of the FSAP, but no information is available concerning the potential regulation of FSAP activity and its metabolism in the vessel wall. In the present study, we demonstrate that the enzymatic activity of FSAP can be inhibited by the serine protease inhibitor, PN-1 (protease nexin-1), that is found in the vasculature. This leads to the loss of the inhibitory effect of FSAP on PDGF-BB-mediated DNA synthesis and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation in VSMCs. The FSAP-PN-1 complexes bind to the LRP (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein) and are subsequently internalized. This binding is inhibited by receptor-associated protein, an antagonist of LRP, as well as heparin. While PDGFbetaR (PDGFbeta receptor) is internalized by an LRP-dependent mechanism after stimulation of cells by PDGF-BB, the FSAP-PN-1 complex neither influenced PDGF-BB-mediated phosphorylation of PDGFbetaR nor its internalization via LRP. Hence, PN-1 inhibits the enzymatic activity of FSAP and neutralizes its effect on PDGF-BB-mediated VSMC proliferation. The FSAP-inhibitor complexes are internalized via LRP without influencing the PDGF-BB signal transduction pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nucleic acids potentiate Factor VII-activating protease (FSAP)-mediated cleavage of platelet-derived growth factor-BB and inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.Biochem J. 2007 May 15;404(1):45-50. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070166. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17300216 Free PMC article.
-
Factor VII-activating protease (FSAP) inhibits growth factor-mediated cell proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells.FASEB J. 2004 Apr;18(6):728-30. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-0898fje. Epub 2004 Feb 20. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 14977886
-
High negative charge-to-size ratio in polyphosphates and heparin regulates factor VII-activating protease.FEBS J. 2009 Sep;276(17):4828-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07183.x. Epub 2009 Jul 31. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19664058
-
Factor VII-activating protease (FSAP): vascular functions and role in atherosclerosis.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Feb;99(2):286-9. doi: 10.1160/TH07-10-0640. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 18278176 Review.
-
Factor VII-Activating Protease: Hemostatic Protein or Immune Regulator?Semin Thromb Hemost. 2018 Mar;44(2):151-158. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1607431. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2018. PMID: 29172215 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the enzymatic activity of the serine protease domain of Factor VII activating protease (FSAP).Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 12;9(1):18990. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55531-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31831842 Free PMC article.
-
Factor VII Activating Protease Expression in Human Platelets and Accumulation in Symptomatic Carotid Plaque.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Sep;9(17):e016445. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016445. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32856552 Free PMC article.
-
PDGF: the nuts and bolts of signalling toolbox.Tumour Biol. 2011 Dec;32(6):1057-70. doi: 10.1007/s13277-011-0212-3. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Tumour Biol. 2011. PMID: 21769672 Review.
-
Origin and diversification of the plasminogen activation system among chordates.BMC Evol Biol. 2019 Jan 17;19(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12862-019-1353-z. BMC Evol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30654737 Free PMC article.
-
Protease Nexin-1 in the Cardiovascular System: Wherefore Art Thou?Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Mar 31;8:652852. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.652852. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33869311 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choi-Miura N. H., Tobe T., Sumiya J., Nakano Y., Sano Y., Mazda T., Tomita M. Purification and characterization of a novel hyaluronan-binding protein (PHBP) from human plasma: it has three EGF, a kringle and a serine protease domain, similar to hepatocyte growth factor activator. J. Biochem. (Tokyo). 1996;119:1157–1165. - PubMed
-
- Kannemeier C., Al-Fakhri N., Preissner K. T., Kanse S. M. Factor VII-activating protease (FSAP) inhibits growth factor-mediated cell proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. Faseb J. 2004;18:728–730. - PubMed
-
- Sedding D., Daniel J. M., Muhl L., Hersemeyer K., Brunsch H., Kemkes-Matthes B., Braun-Dullaeus R. C., Tillmanns H., Weimer T., Preissner K. T., Kanse S. M. The G534E polymorphism of the gene encoding the factor VII-activating protease is associated with cardiovascular risk due to increased neointima formation. J. Exp. Med. 2006;203:2801–2807. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choi-Miura N. H., Takahashi K., Yoda M., Saito K., Mazda T., Tomita M. Proteolytic activation and inactivation of the serine protease activity of plasma hyaluronan binding protein. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001;24:448–452. - PubMed
-
- Kannemeier C., Feussner A., Stohr H. A., Weisse J., Preissner K. T., Romisch J. Factor VII and single-chain plasminogen activator-activating protease: activation and autoactivation of the proenzyme. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001;268:3789–3796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

