Micro-field evoked potentials recorded from the porcine sub-dural cortical surface utilizing a microelectrode array
- PMID: 17298849
- PMCID: PMC2223486
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.01.004
Micro-field evoked potentials recorded from the porcine sub-dural cortical surface utilizing a microelectrode array
Abstract
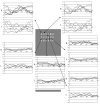
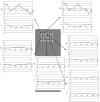
A sub-dural surface microelectrode array designed to detect micro-field evoked potentials has been developed. The device is comprised of an array of 350-microm square gold contacts, with bidirectional spacing of 150 microm, contained within a polyimide Kapton material. Cytotoxicity testing suggests that the device is suitable for use with animal and human patients. Implementation of the device in animal studies revealed that reliable evoked potentials could be acquired. Further work will be needed to determine how these micro-field potentials, which demonstrate selectivity for one eye, relate to the distribution of the ocular dominance columns of the occipital cortex.
Figures




References
-
- Bernadette F. Stereotaxic atlas of the pig brain. Brain Res. Bull. 1999;49:1–138. - PubMed
-
- Black J. Biological Performance of Materials: Fundamentals of Biocompatibilty. Marcel Dekker, Inc; New York: 1999. pp. 323–425.
-
- Bugbee NM, Goldmann-Rakic P. Columnar organization of cortico-cortical projections in squirrel and rhesus monkey: similarity of column width in species differing in cortical volume. J. Comp. Neurol. 1983;220:355–64. - PubMed
-
- Eckhorn R, Stett A, Schanze T, Gekeler F, Schwahn H, Zrenner E, Wilms M, Eger M, Hesse L. Physiological functional evaluation of retinal implants in animal models. Ophthalmologe: Zeischrift der Deutschen Ophthalmologischen Gesellschaft. 2001;98:369–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

