Fibroblast growth factor blocks Sonic hedgehog signaling in neuronal precursors and tumor cells
- PMID: 17299056
- PMCID: PMC1815291
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0605770104
Fibroblast growth factor blocks Sonic hedgehog signaling in neuronal precursors and tumor cells
Abstract
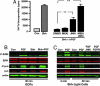
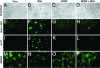
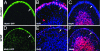
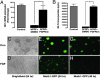
The Sonic hedgehog (Shh) and FGF signaling pathways regulate growth and differentiation in many regions of the nervous system, but interactions between these pathways have not been studied extensively. Here, we examine the relationship between Shh and FGF signaling in granule cell precursors (GCPs), which are the most abundant neural progenitors in the cerebellum and the putative cell of origin for the childhood brain tumor medulloblastoma. In these cells, Shh induces a potent proliferative response that is abolished by coincubation with basic FGF. FGF also inhibits transcription of Shh target genes and prevents activation of a Gli-responsive promoter in fibroblasts, which suggests that it blocks Shh signaling upstream of Gli-mediated transcription. FGF-mediated inhibition of Shh responses requires activation of FGF receptors and of ERK and JNK kinases, because it can be blocked by inhibitors of these enzymes. Finally, FGF promotes differentiation of GCPs in vitro and in vivo and halts proliferation of tumor cells from patched (ptc) mutant mice, a model for medulloblastoma. These findings suggest that FGF is a potent inhibitor of Shh signaling and may be a useful therapy for tumors involving activation of the hedgehog pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
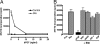
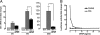
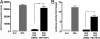
Similar articles
-
Differential gene induction by genetic and ligand-mediated activation of the Sonic hedgehog pathway in neural stem cells.Dev Biol. 2007 Aug 15;308(2):331-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.05.031. Epub 2007 May 31. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17599824
-
Distinct roles for fibroblast growth factor signaling in cerebellar development and medulloblastoma.Oncogene. 2013 Aug 29;32(35):4181-8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.440. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23045271 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional profiling of the Sonic hedgehog response: a critical role for N-myc in proliferation of neuronal precursors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jun 10;100(12):7331-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0832317100. Epub 2003 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12777630 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of oligodendrocyte progenitors in dorsal forebrain by intraventricular microinjection of FGF-2.Dev Biol. 2006 Sep 1;297(1):262-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.05.017. Epub 2006 May 19. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16782086
-
Sonic hedgehog signaling during adrenal development.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Mar 31;351(1):19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.10.002. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22020162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transient inhibition of the ERK pathway prevents cerebellar developmental defects and improves long-term motor functions in murine models of neurofibromatosis type 1.Elife. 2014 Dec 23;3:e05151. doi: 10.7554/eLife.05151. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25535838 Free PMC article.
-
RAS/MAPK Activation Drives Resistance to Smo Inhibition, Metastasis, and Tumor Evolution in Shh Pathway-Dependent Tumors.Cancer Res. 2015 Sep 1;75(17):3623-35. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2999-T. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26130651 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional regulation of postmitotic H3K27me3 distributions underlie cerebellar granule neuron maturation dynamics.Elife. 2023 Apr 24;12:e86273. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86273. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37092728 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of glycosyltransferase 8 domain containing 2 confers ovarian cancer to CDDP resistance by activating FGFR/PI3K signalling axis.Oncogenesis. 2021 Jul 22;10(7):55. doi: 10.1038/s41389-021-00343-w. Oncogenesis. 2021. PMID: 34294681 Free PMC article.
-
Zhangfei induces the expression of the nerve growth factor receptor, trkA, in medulloblastoma cells and causes their differentiation or apoptosis.J Neurooncol. 2009 Jan;91(1):7-17. doi: 10.1007/s11060-008-9682-6. Epub 2008 Aug 22. J Neurooncol. 2009. PMID: 18719857
References
-
- Cayuso J, Marti E. J Neurobiol. 2005;64:376–387. - PubMed
-
- Fogarty MP, Kessler JD, Wechsler-Reya RJ. J Neurobiol. 2005;64:458–475. - PubMed
-
- Echelard Y, Epstein DJ, St-Jacques B, Shen L, Mohler J, McMahon JA, McMahon AP. Cell. 1993;75:1417–1430. - PubMed
-
- Roelink H, Augsburger A, Heemskerk J, Korzh V, Norlin S, Ruiz i Altaba A, Tanabe Y, Placzek M, Edlund T, Jessell TM, et al. Cell. 1994;76:761–775. - PubMed
-
- Marti E, Bovolenta P. Trends Neurosci. 2002;25:89–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

