Adalimumab for maintenance treatment of Crohn's disease: results of the CLASSIC II trial
- PMID: 17299059
- PMCID: PMC2701613
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.106781
Adalimumab for maintenance treatment of Crohn's disease: results of the CLASSIC II trial
Abstract
Background: Adalimumab induced clinical remission after four weeks in patients with active Crohn's disease in the CLASSIC I trial.
Objective: To evaluate long term efficacy and safety of adalimumab maintenance therapy in Crohn's disease in a follow-on randomised controlled trial (CLASSIC II).
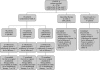
Methods: In the preceding CLASSIC I trial, 299 patients with moderate to severe Crohn's disease naive to tumour necrosis factor antagonists received induction therapy with adalimumab 40 mg/20 mg, 80 mg/40 mg, or 160 mg/80 mg, or placebo, at weeks 0 and 2. In all, 276 patients from CLASSIC I enrolled in CLASSIC II and received open-label adalimumab 40 mg at weeks 0 (week 4 of CLASSIC I) and 2; 55 patients in remission at both weeks 0 and 4 were re-randomised to adalimumab 40 mg every other week, 40 mg weekly, or placebo for 56 weeks. Patients not in remission at both weeks 0 and 4 were enrolled in an open-label arm and received adalimumab 40 mg every other week. With non-response or flare, these patients could have their dosages increased to 40 mg weekly. Patients in the randomised arm with continued non-response or disease flare could switch to open-label adalimumab 40 mg every other week and again to 40 mg weekly. The primary end point was maintenance of remission (CDAI <150) in randomised patients through week 56.
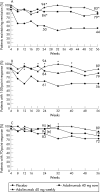
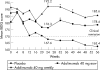
Results: Of 55 patients randomised at week 4, 79% who received adalimumab 40 mg every other week and 83% who received 40 mg weekly were in remission at week 56, v 44% for placebo (p<0.05). In all, 204 patients entered the open-label arm. Of these, 93 (46%) were in clinical remission at week 56. Adalimumab was generally well-tolerated in all patients.
Conclusions: Adalimumab induced and maintained clinical remission for up to 56 weeks in patients with moderate to severe Crohn's disease naive to anti-TNF treatment.
Comment in
-
The classics in perspective.Gut. 2007 Sep;56(9):1184-6. doi: 10.1136/gut.2007.121830. Gut. 2007. PMID: 17698863 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Adalimumab-induced lupus erythematosus in Crohn's disease patients previously treated with infliximab.Gut. 2008 Apr;57(4):559; author reply 559-60. Gut. 2008. PMID: 18334664 No abstract available.
-
Fatal invasive pulmonary aspergillosis associated with adalimumab therapy.Gut. 2009 Jan;58(1):149. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.161638. Gut. 2009. PMID: 19091839 No abstract available.
References
-
- Romagnani S. Th1/Th2 cells. Inflamm Bowel Dis 19995285–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical