Bortezomib enhances dendritic cell (DC)-mediated induction of immunity to human myeloma via exposure of cell surface heat shock protein 90 on dying tumor cells: therapeutic implications
- PMID: 17299090
- PMCID: PMC1885516
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-054221
Bortezomib enhances dendritic cell (DC)-mediated induction of immunity to human myeloma via exposure of cell surface heat shock protein 90 on dying tumor cells: therapeutic implications
Abstract
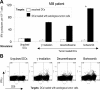
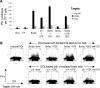
Most anticancer chemotherapies are immunosuppressive and induce nonimmunogenic tumor cell death. Bortezomib, a specific inhibitor of 26S proteasome, has shown clinical activity in several human tumors, including myeloma. Here we show that the uptake of human myeloma cells by dendritic cells (DCs) after tumor cell death by bortezomib, but not gamma irradiation or steroids, leads to the induction of antitumor immunity, including against primary tumor cells, without the need for any additional adjuvants. The delivery of activating signal from bortezomib-killed tumor cells to DCs depends on cell-cell contact between DCs and dying tumor cells and is mediated by bortezomib-induced exposure of heat shock protein 90 (hsp90) on the surface of dying cells. The combination of bortezomib and geldanamycin (an hsp90 inhibitor) leads to greater apoptosis of tumor cells but abrogates their immunogenicity. These data identify drug-induced exposure of endogenous heat shock proteins on the surface of dying cells as a mechanism of immunogenic death of human tumors. Specific targeting of bortezomib to tumors may enhance their immunogenicity and the induction of antitumor immunity.
Figures
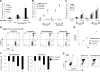


References
-
- Lake RA, van der Most RG. A better way for a cancer cell to die. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2503–2504. - PubMed
-
- Lake RA, Robinson BW. Immunotherapy and chemotherapy—a practical partnership. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:397–405. - PubMed
-
- Zitvogel L, Casares N, Pequignot MO, Chaput N, Albert ML, Kroemer G. Immune response against dying tumor cells. Adv Immunol. 2004;84:131–179. - PubMed
-
- Adams J. The proteasome: a suitable antineoplastic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:349–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

