Time-dependent spectral analysis of epidemiological time-series with wavelets
- PMID: 17301013
- PMCID: PMC2373388
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2007.0212
Time-dependent spectral analysis of epidemiological time-series with wavelets
Abstract
In the current context of global infectious disease risks, a better understanding of the dynamics of major epidemics is urgently needed. Time-series analysis has appeared as an interesting approach to explore the dynamics of numerous diseases. Classical time-series methods can only be used for stationary time-series (in which the statistical properties do not vary with time). However, epidemiological time-series are typically noisy, complex and strongly non-stationary. Given this specific nature, wavelet analysis appears particularly attractive because it is well suited to the analysis of non-stationary signals. Here, we review the basic properties of the wavelet approach as an appropriate and elegant method for time-series analysis in epidemiological studies. The wavelet decomposition offers several advantages that are discussed in this paper based on epidemiological examples. In particular, the wavelet approach permits analysis of transient relationships between two signals and is especially suitable for gradual change in force by exogenous variables.
Figures

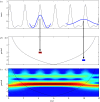
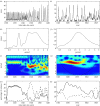
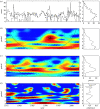
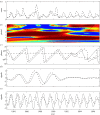
References
-
- Anderson R.M, May R.M. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 1991. Infectious diseases of humans.
-
- Andrieu C, Doucet A, Fitzgerald W.J. An introduction to Monte Carlo methods for Bayesian data analysis. In: Mees A.I, editor. Nonlinear dynamics and statistics. Birkhäusser; Boston, MA: 2001. pp. 169–217.
-
- Aron J.L, Schwartz I.R. Seasonality and period-doubling bifurcations in an epidemic model. J. Theor. Biol. 1984;110:665–679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
