The relationship between optical coherence tomography and scanning laser polarimetry measurements in glaucoma
- PMID: 17302208
- PMCID: PMC2908856
- DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2006.20.4.225
The relationship between optical coherence tomography and scanning laser polarimetry measurements in glaucoma
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the relationship between optical coherence tomography (OCT) and scanning laser polarimetry (SLP) in measuring peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness in glaucomatous eyes.
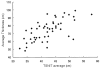
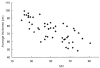
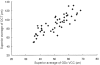
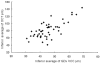
Methods: Fifty glaucomatous eyes were evaluated in this study. Evaluations were analyzed two ways. First, parameters of the Stratus OCT (average thickness, superior/inferior average) and GDx VCC (TSNIT average, nerve fiber indicator (NFI), superior/inferior average) were correlated using the Pearson's correlation coefficient (r). Secondly, comparison (r) of these parameters was completed using the mean deviation (MD) of visual field defect.
Results: The following parameters were found to be significantly correlated (P < 0.005). TSNIT average/average thickness (r = 0.673), NFI/average thickness (r = -0.742), superior average (r = 0.841), and inferior average (r = 0.736). In the correlation analysis using the severity of visual field defect, all these parameters had statistically meaningful correlations (P < 0.005).
Conclusions: GDx VCC and Stratus OCT are highly correlated in glaucomatous eyes. Therefore, peripapillary RNFL thickness measured by Stratus OCT and GDx VCC may be equally helpful in the diagnosis of glaucoma.
Figures
References
-
- Kerrgan-Baumrind LA, Quigley HA, Pease ME, et al. Number of ganglion cells in glaucoma eyes compared with threshold visual field tests in the same persons. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:741–748. - PubMed
-
- Quigley HA, Addicks EM, Green WR. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. III. Quantitative correlation of nerve fiber loss and visual field defect in glaucoma, ischemic neuropathy, papilledema, and toxic neuropathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982;100:135–146. - PubMed
-
- Tuulonen A, Airaksinen PJ. Initial glaucomatous optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer abnormalities and their progression. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991;111:485–490. - PubMed
-
- Quigley HA, Miller NR, George T. Clinical evaluation of nerve fiber layer atrophy as an indicator of glaucomatous optic nerve damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980;98:1564–1571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical