Low numbers of regulatory T cells in common variable immunodeficiency: association with chronic inflammation in vivo
- PMID: 17302902
- PMCID: PMC1810487
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03314.x
Low numbers of regulatory T cells in common variable immunodeficiency: association with chronic inflammation in vivo
Abstract
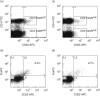
Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is a heterogeneous syndrome characterized by defective immunoglobulin production and high frequency of bacterial infections, autoimmunity and manifestations of chronic inflammation. Abnormalities of CD4+CD25high forkhead box P3 (FoxP3)+ regulatory T cells (Treg) have been associated with autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, and we hypothesized that CVID might be characterized by Treg abnormalities. CD3+ cells from patients and controls were analysed for the expression of FoxP3 mRNA by real time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from CVID patients and controls were stained for Treg markers, analysed by flow cytometry and compared to clinical characteristics. The main findings were: (i) CVID patients had significantly decreased expression of FoxP3 mRNA and decreased proportions of CD4+CD25highFoxP3+ cells compared to controls; (ii) CVID patients with splenomegaly had even lower proportions of Treg compared to other patients and controls; (iii) serum levels of the inflammatory marker neopterin were correlated negatively with the proportions of Treg within the CVID population, while there was no significant association with bronchiectasis. We have demonstrated decreased proportions of Treg in CVID patients, particularly in those with signs of chronic inflammation. Decreased proportions of TReg are suggested to be pathogenetically important in autoimmunity, and our results suggest that TReg may have a similar role in CVID.
Figures


References
-
- Di Renzo M, Pasqui AL, Auteri A. Common variable immunodeficiency: a review. Clin Exp Med. 2004;3:211–7. - PubMed
-
- Brandt D, Gershwin ME. Common variable immune deficiency and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2006;5:465–70. - PubMed
-
- Maloy KJ, Powrie F. Regulatory T cells in the control of immune pathology. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:816–22. - PubMed
-
- Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003;299:1057–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

