Effects of flecainide and quinidine on arrhythmogenic properties of Scn5a+/- murine hearts modelling the Brugada syndrome
- PMID: 17303635
- PMCID: PMC2075209
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.128785
Effects of flecainide and quinidine on arrhythmogenic properties of Scn5a+/- murine hearts modelling the Brugada syndrome
Abstract
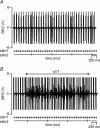
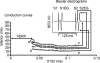
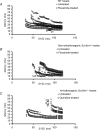
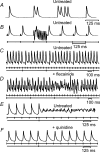
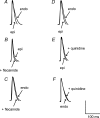
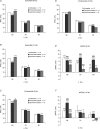
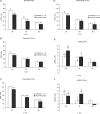
Brugada syndrome (BrS) is associated with a loss of Na+ channel function and an increased incidence of rapid polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) and sudden cardiac death. A programmed electrical stimulation (PES) technique assessed arrhythmic tendency in Langendorff-perfused wild-type (WT) and genetically modified (Scn5a+/-) 'loss-of-function' murine hearts in the presence and absence of flecainide and quinidine, and the extent to which Scn5a+/- hearts model the human BrS. Extra-stimuli (S2), applied to the right ventricular epicardium, followed trains of pacing stimuli (S1) at progressively reduced S1-S2 intervals. These triggered VT in 16 out of 29 untreated Scn5a+/- and zero out of 31 WT hearts. VT occurred in 11 out of 16 (10 microM) flecainide-treated WT and nine out of the 13 initially non-arrhythmogenic Scn5a+/- hearts treated with (1.0 microM) flecainide. Quinidine (10 microM) prevented VT in six out of six flecainide-treated WT and 13 out of the 16 arrhythmogenic Scn5a+/- hearts in parallel with its clinical effects. Paced electrogram fractionation analysis demonstrated increased electrogram durations, expressed as electrogram duration (EGD) ratios, with shortening S1-S2 intervals in arrhythmogenic Scn5a+/- hearts, and prolonged ventricular effective refractory periods (VERPs) in non-arrhythmogenic Scn5a+/- hearts. Flecainide increased EGD ratios in WT (at 10 microM) and non-arrhythmogenic Scn5a+/- hearts (at 1.0 microM), whereas quinidine (10 microM) reduced EGD ratios and prolonged VERPs in WT and arrhythmogenic Scn5a+/- hearts. However, epicardial and endocardial monophasic action potential recordings consistently demonstrated positive gradients of repolarization in WT, arrhythmogenic and non-arrhythmogenic Scn5a+/- hearts under all pharmacological conditions. Together, these findings demonstrate proarrhythmic effects of flecainide in WT and Scn5a+/- murine hearts that recapitulate its clinical effects. They further attribute the arrhythmogenic phenomena observed here to re-entrant substrates resulting from delayed epicardial activation despite an absence of transmural heterogeneities of repolarization, in sharp contrast to recent characterizations in 'gain-of-function' Scn5a+/Delta murine hearts modelling the long-QT(3) syndrome.
Figures




References
-
- Akar FG, Wu RC, Deschenes I, Armoundas AA, Piacentino V, 3rd, Houser SR, Tomaselli GF. Phenotypic differences in transient outward K+ current of human and canine ventricular myocytes: insights into molecular composition of ventricular Ito. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286:H602–H609. - PubMed
-
- Alings M, Dekker L, Sadee A, Wilde A. Quinidine-induced electrocardiographic normalization in two patients with Brugada syndrome. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2001;24:1420–1422. - PubMed
-
- Alings M, Wilde A. ‘Brugada’ syndrome: clinical data and suggested pathophysiological mechanism. Circulation. 1999;99:666–673. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JL, Platia EV, Hallstrom A, Henthorn RW, Buckingham TA, Carlson MD, Carson PE. Interaction of baseline characteristics with the hazard of encainide, flecainide, and moricizine therapy in patients with myocardial infarction. A possible explanation for increased mortality in the Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST) Circulation. 1994;90:2843–2852. - PubMed
-
- Anno T, Hondeghem LM. Interactions of flecainide with guinea pig cardiac sodium channels. Importance of activation unblocking to the voltage dependence of recovery. Circ Res. 1990;66:789–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

