Yeast functional genomic screens lead to identification of a role for a bacterial effector in innate immunity regulation
- PMID: 17305427
- PMCID: PMC1797620
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030021
Yeast functional genomic screens lead to identification of a role for a bacterial effector in innate immunity regulation
Abstract
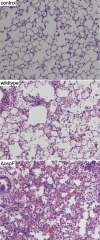
Numerous bacterial pathogens manipulate host cell processes to promote infection and ultimately cause disease through the action of proteins that they directly inject into host cells. Identification of the targets and molecular mechanisms of action used by these bacterial effector proteins is critical to understanding pathogenesis. We have developed a systems biological approach using the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae that can expedite the identification of cellular processes targeted by bacterial effector proteins. We systematically screened the viable yeast haploid deletion strain collection for mutants hypersensitive to expression of the Shigella type III effector OspF. Statistical data mining of the results identified several cellular processes, including cell wall biogenesis, which when impaired by a deletion caused yeast to be hypersensitive to OspF expression. Microarray experiments revealed that OspF expression resulted in reversed regulation of genes regulated by the yeast cell wall integrity pathway. The yeast cell wall integrity pathway is a highly conserved mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, normally activated in response to cell wall perturbations. Together these results led us to hypothesize and subsequently demonstrate that OspF inhibited both yeast and mammalian MAPK signaling cascades. Furthermore, inhibition of MAPK signaling by OspF is associated with attenuation of the host innate immune response to Shigella infection in a mouse model. These studies demonstrate how yeast systems biology can facilitate functional characterization of pathogenic bacterial effector proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Shigella flexneri type III secreted effector OspF reveals new crosstalks of proinflammatory signaling pathways during bacterial infection.Cell Signal. 2011 Jul;23(7):1188-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.03.006. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21402152
-
OspF and OspC1 are Shigella flexneri type III secretion system effectors that are required for postinvasion aspects of virulence.Infect Immun. 2006 Oct;74(10):5964-76. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00594-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16988276 Free PMC article.
-
The Shigella type three secretion system effector OspF invades host nucleus by binding host importin α1.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Apr 22;35(5):71. doi: 10.1007/s11274-019-2635-8. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31011826
-
Yeast as a Heterologous Model System to Uncover Type III Effector Function.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Feb 25;12(2):e1005360. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005360. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 26914889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a versatile model system for the identification and characterization of bacterial virulence proteins.Cell Host Microbe. 2008 Jul 17;4(1):8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.06.004. Cell Host Microbe. 2008. PMID: 18621006 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying Pseudomonas syringae Type III Secreted Effector Function via a Yeast Genomic Screen.G3 (Bethesda). 2019 Feb 7;9(2):535-547. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200877. G3 (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 30573466 Free PMC article.
-
The Shigella type three secretion system effector OspG directly and specifically binds to host ubiquitin for activation.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57558. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057558. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469023 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Legionella pneumophila effectors regulated by the LetAS-RsmYZ-CsrA regulatory cascade, many of which modulate vesicular trafficking.J Bacteriol. 2014 Feb;196(3):681-92. doi: 10.1128/JB.01175-13. Epub 2013 Nov 22. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24272784 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of small molecule inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S using a yeast phenotypic screen.PLoS Genet. 2008 Feb 29;4(2):e1000005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000005. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18454192 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel Coxiella burnetii Icm/Dot effectors and genetic analysis of their involvement in modulating a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.Infect Immun. 2014 Sep;82(9):3740-52. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01729-14. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24958706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galán JE, Collmer A. Type III secretion machines: Bacterial devices for protein delivery into host cells. Science. 1999;284:1322–1328. - PubMed
-
- Campodonico EM, Chesnel L, Roy CR. A yeast genetic system for the identification and characterization of substrate proteins transferred into host cells by the Legionella pneumophila Dot/Icm system. Mol Microbiol. 2005;56:918–933. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

