Nodal signaling activates differentiation genes during zebrafish gastrulation
- PMID: 17306247
- PMCID: PMC1885460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.01.012
Nodal signaling activates differentiation genes during zebrafish gastrulation
Abstract
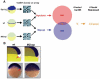
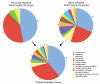
Nodal signals induce mesodermal and endodermal progenitors during vertebrate development. To determine the role of Nodal signaling at a genomic level, we isolated Nodal-regulated genes by expression profiling using macroarrays and gene expression databases. Putative Nodal-regulated genes were validated by in situ hybridization screening in wild type and Nodal signaling mutants. 46 genes were identified, raising the currently known number of Nodal-regulated genes to 72. Based on their expression patterns along the dorsoventral axis, most of these genes can be classified into two groups. One group is expressed in the dorsal margin, whereas the other group is expressed throughout the margin. In addition to transcription factors and signaling components, the screens identified several new functional classes of Nodal-regulated genes, including cytoskeletal components and molecules involved in protein secretion or endoplasmic reticulum stress. We found that x-box binding protein-1 (xbp1) is a direct target of Nodal signaling and required for the terminal differentiation of the hatching gland, a specialized secretory organ whose specification is also dependent on Nodal signaling. These results indicate that Nodal signaling regulates not only specification genes but also differentiation genes.
Figures
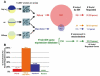
 ) was calculated by extrapolation. Clones identified by differential hybridization were significantly enriched compared to random clone picking.
) was calculated by extrapolation. Clones identified by differential hybridization were significantly enriched compared to random clone picking.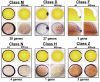

Similar articles
-
A novel sox gene, 226D7, acts downstream of Nodal signaling to specify endoderm precursors in zebrafish.Mech Dev. 2001 Sep;107(1-2):25-38. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(01)00453-1. Mech Dev. 2001. PMID: 11520661
-
Genes dependent on zebrafish cyclops function identified by AFLP differential gene expression screen.Genesis. 2000 Jan;26(1):86-97. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1526-968x(200001)26:1<86::aid-gene11>3.0.co;2-q. Genesis. 2000. PMID: 10660676
-
Identification of nodal signaling targets by array analysis of induced complex probes.Dev Dyn. 2001 Dec;222(4):571-80. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.1220. Dev Dyn. 2001. PMID: 11748827
-
Vertebrate development: the fast track to nodal signalling.Curr Biol. 2000 Nov 16;10(22):R843-6. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00789-2. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 11102828 Review.
-
Nodal signaling and the evolution of deuterostome gastrulation.Dev Dyn. 2005 Oct;234(2):269-78. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20549. Dev Dyn. 2005. PMID: 16127715 Review.
Cited by
-
Scale-invariant patterning by size-dependent inhibition of Nodal signalling.Nat Cell Biol. 2018 Sep;20(9):1032-1042. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0155-7. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Nat Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30061678 Free PMC article.
-
Gene module reconstruction identifies cellular differentiation processes and the regulatory logic of specialized secretion in zebrafish.Dev Cell. 2025 Feb 24;60(4):581-598.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.10.015. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Dev Cell. 2025. PMID: 39591963 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol Effects on Early Developmental Stages Studied Using the Zebrafish.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 13;10(10):2555. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102555. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isthmin-A Multifaceted Protein Family.Cells. 2022 Dec 21;12(1):17. doi: 10.3390/cells12010017. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene module reconstruction elucidates cellular differentiation processes and the regulatory logic of specialized secretion.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 29:2023.12.29.573643. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.29.573643. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Dev Cell. 2025 Feb 24;60(4):581-598.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.10.015. PMID: 38234833 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Adams JC. Roles of fascin in cell adhesion and motility. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:590–6. - PubMed
-
- Agathon A, Thisse B, Thisse C. Morpholino knock-down of antivin1 and antivin2 upregulates nodal signaling. Genesis. 2001;30:178–82. - PubMed
-
- Alexander J, Rothenberg M, Henry GL, Stainier DY. casanova plays an early and essential role in endoderm formation in zebrafish. Dev Biol. 1999;215:343–57. - PubMed
-
- Alexander J, Stainier DY. A molecular pathway leading to endoderm formation in zebrafish. Curr Biol. 1999;9:1147–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

