Functional characterization of the Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein by transposon linker-insertion mutagenesis
- PMID: 17306321
- PMCID: PMC1959473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.01.006
Functional characterization of the Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein by transposon linker-insertion mutagenesis
Abstract
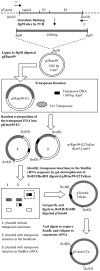
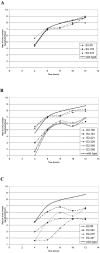
The glycoprotein envelope of alphaviruses consists of two proteins, E1 and E2. E1 is responsible for fusion and E2 is responsible for receptor binding. An atomic structure is available for E1, but one for E2 has not been reported. In this study, transposon linker-insertion mutagenesis was used to probe the function of different domains of E2. A library of mutants, containing 19 amino acid insertions in the E2 glycoprotein sequence of the prototype alphavirus, Sindbis virus (SINV), was generated. Fifty-seven independent E2 insertions were characterized, of which more than half (67%) gave rise to viable virus. The wild-type-like mutants identify regions that accommodate insertions without perturbing virus production and can be used to insert targeting moieties to direct SINV to specific receptors. The defective and lethal mutants give insight into regions of E2 important for protein stability, transport to the cell membrane, E1-E2 contacts, and receptor binding.
Figures

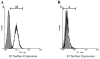

References
-
- Chikkanna-Gowda CP, Sheahan BJ, Fleeton MN, Atkins GJ. Regression of mouse tumours and inhibition of metastases following administration of a Semliki Forest virus vector with enhanced expression of IL-12. Gene Ther. 2005;12(16):1253–63. - PubMed
-
- Choi HK, Tong L, Minor W, Dumas P, Boege U, Rossmann MG, Wengler G. Structure of Sindbis virus core protein reveals a chymotrypsin-like serine proteinase and the organization of the virion. Nature. 1991;354:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Davis NL, Pence DF, Meyer WJ, Schmaljohn AL, Johnston RE. Alternative forms of a strain-specific neutralizing antigenic site on the Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein. Virology. 1987;161(1):101–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

