Ubiquitination of RIP1 regulates an NF-kappaB-independent cell-death switch in TNF signaling
- PMID: 17306544
- PMCID: PMC1868513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.01.027
Ubiquitination of RIP1 regulates an NF-kappaB-independent cell-death switch in TNF signaling
Abstract
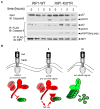
TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1) can trigger opposing responses within the same cell: a prosurvival response or a cell-death pathway [1, 2]. Cell survival requires NF-kappaB-mediated transcription of prosurvival genes [3-9]; apoptosis occurs if NF-kappaB signaling is blocked [5, 7-9]. Hence, activation of NF-kappaB acts as a cell-death switch during TNF signaling. This study demonstrates that the pathway includes another cell-death switch that is independent of NF-kappaB. We show that lysine 63-linked ubiquitination of RIP1 on lysine 377 inhibits TNF-induced apoptosis first through an NF-kappaB-independent mechanism and, subsequently, through an NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism. In contrast, in the absence of ubiquitination, RIP1 serves as a proapoptotic signaling molecule by engaging CASPASE-8. Therefore, RIP1 is a dual-function molecule that can be either prosurvival or prodeath depending on its ubiquitination state, and this serves as an NF-kappaB-independent cell-death switch early in TNF signaling. These results provide an explanation for the conflicting reports on the role of RIP1 in cell death; this role was previously suggested to be both prosurvival and prodeath [10-12]. Because TRAF2 is the E3 ligase for RIP1 [13], these observations provide an explanation for the NF-kappaB-independent antiapoptotic function previously described for TRAF2 [14-16].
Figures



References
-
- Micheau O, Tschopp J. Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell. 2003;114:181–190. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal BB. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:745–756. - PubMed
-
- Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin AS., Jr NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science. 1998;281:1680–1683. - PubMed
-
- Wang CY, Mayo MW, Baldwin AS., Jr TNF- and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Science. 1996;274:784–787. - PubMed
-
- Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Kafri T, Green DR, Verma IM. Suppression of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB. Science. 1996;274:787–789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

