The equine herpesvirus-1 IR3 gene that lies antisense to the sole immediate-early (IE) gene is trans-activated by the IE protein, and is poorly expressed to a protein
- PMID: 17306852
- PMCID: PMC1939811
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.01.024
The equine herpesvirus-1 IR3 gene that lies antisense to the sole immediate-early (IE) gene is trans-activated by the IE protein, and is poorly expressed to a protein
Abstract
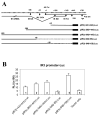
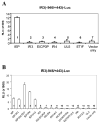
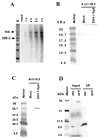
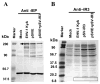
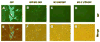
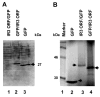
The unique IR3 gene of equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1) is expressed as a late 1.0-kb transcript. Previous studies confirmed the IR3 transcription initiation site and tentatively identified other cis-acting elements specific to IR3 such as a TATA box, a 443 base pair 5'untranslated region (UTR), a 285 base pair open reading frame (ORF), and a poly adenylation (A) signal [Holden, V.R., Harty, R.N., Yalamanchili, R.R., O'Callaghan, D.J., 1992. The IR3 gene of equine herpesvirus type 1: a unique gene regulated by sequences within the intron of the immediate-early gene. DNA Seq. 3, 143-152]. Transient transfection assays revealed that the IR3 promoter is strongly trans-activated by the IE protein (IEP) and that coexpression of the IEP with the early EICP0 and IR4 regulatory proteins results in maximal trans-activation of the IR3 promoter. Gel shift assays revealed that the IEP directly binds to the IR3 promoter region. Western blot analysis showed that the IR3 protein produced in E. coli was detected by antibodies to IR3 synthetic peptides; however, the IR3 protein was not detected in EHV-1 infected cell extracts by these same anti-IR3 antibodies, even though the IR3 transcript was detected by northern blot. These findings suggest that the IR3 may not be expressed to a protein. Expression of an IR3/GFP fusion gene was not observed, but expression of a GFP/IR3 fusion gene was detected by fluorescent microscopy. In further attempts to detect the IR3/GFP fusion protein using anti-GFP antibody, western blot analysis showed that the IR3/GFP fusion protein was not detected in vivo. Interestingly, a truncated form of the GFP/IR3 protein was synthesized from the GFP/IR3 fusion gene. However, GFP/IR3 and IR3/GFP fusion proteins of the predicted sizes were synthesized by in vitro coupled transcription and translation of the fusion genes, suggesting poor expression of the IR3 protein in vivo. The possible role of the IR3 transcript in EHV-1 infection is discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Alam J, Cook JL. Reporter genes: application to the study of mammalian gene transcription. Anal Biochem. 1990;188:245–254. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht RA, Jang HK, Kim SK, O’Callaghan DJ. Direct interaction of TFIIB and the IE protein of equine herpesvirus 1 is required for maximal trans- activation function. Virology. 2003;316:302–312. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht RA, Kim SK, O’Callaghan DJ. The EICP27 protein of equine herpesvirus 1 is recruited to viral promoters by its interaction with the immediate-early protein. Virology. 2005;333:74–87. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht RA, Kim SK, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, O’Callaghan DJ. The equine herpesvirus 1 EICP27 protein enhances gene expression via an interaction with TATA box-binding protein. Virology. 2004;324:311–326. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

