The complete nuclear estrogen receptor family in the rainbow trout: discovery of the novel ERalpha2 and both ERbeta isoforms
- PMID: 17307310
- PMCID: PMC1868691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.12.030
The complete nuclear estrogen receptor family in the rainbow trout: discovery of the novel ERalpha2 and both ERbeta isoforms
Abstract
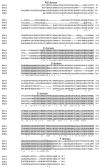
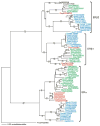
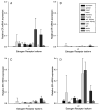
Estrogen hormones interact with cellular ERs to exert their biological effects in vertebrate animals. Similar to other animals, fishes have two distinct ER subtypes, ERalpha (NR3A1) and ERbeta (NR3A2). The ERbeta subtype is found as two different isoforms in several fish species because of a gene duplication event. Although predicted, two different isoforms of ERalpha have not been demonstrated in any fish species. In the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), the only ER described is an isoform of the ERalpha subtype (i.e. ERalpha1, NR3A1a). The purpose of this study was to determine whether the gene for the other ERalpha isoform, ERalpha2 (i.e., NR3A1b), exists in the rainbow trout. A RT-PCR and cloning strategy, followed by screening a rainbow trout BAC library yielded a unique DNA sequence coding for 558 amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence had a 75.4% overall similarity to ERalpha1. Both the rainbow trout ERbeta subtypes, ERbeta1 [NR3A2a] and ERbeta2, [NR3A2b] which were previously unknown in this species, were also sequenced as part of this study, and the amino acid sequences were found to be very different from the ERalphas (approximately 40% similarity). ERbeta1 and ERbeta2 had 594 and 604 amino acids, respectively, and had 57.6% sequence similarity when compared to one another. This information provides what we expect to be the first complete nuclear ER gene family in a fish. A comprehensive phylogenetic analysis with all other known fish ER gene sequences was undertaken to understand the evolution of fish ERs. The results show a single ERalpha subtype clade, with the closest relative to rainbow trout ERalpha2 being rainbow trout ERalpha1, suggesting a recent, unique duplication event to create these two isoforms. For the ERbeta subtype there are two distinct subclades, one represented by the ERbeta1 isoform and the other by the ERbeta2 isoform. The rainbow trout ERbeta1 and ERbeta2 are not closely associated with each other, but instead fall into their respective ERbeta subclades with other known fish species. Real-time RT-PCR was used to measure the mRNA levels of all four ER isoforms (ERalpha1, ERalpha2, ERbeta1, and ERbeta2) in stomach, spleen, heart, brain, pituitary, muscle, anterior kidney, posterior kidney, liver, gill, testis and ovary samples from rainbow trout. The mRNAs for each of the four ERs were detected in every tissue examined. The liver tended to have the highest ER mRNA levels along with the testes, while the lowest levels were generally found in the stomach or heart. The nuclear ERs have a significant and ubiquitous distribution in the rainbow trout providing the potential for complex interactions that involve the functioning of many organ systems.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of hepatic estrogen receptor isoform mRNA expression in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2009 Mar;161(1):73-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.11.022. Epub 2008 Dec 3. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19084018
-
Expression of estrogen receptors in female rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during first ovarian development and under dense rearing condition.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2018 Apr 1;259:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 7. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29017850
-
Molecular cloning of two isoforms of Xenopus (Silurana) tropicalis estrogen receptor mRNA and their expression during development.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Mar;1769(3):172-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2007.01.011. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17346814
-
ERbeta in breast cancer--onlooker, passive player, or active protector?Steroids. 2008 Oct;73(11):1039-51. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2008.04.006. Epub 2008 Apr 20. Steroids. 2008. PMID: 18501937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptor beta in the brain: from form to function.Brain Res Rev. 2008 Mar;57(2):309-20. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2007.05.013. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Brain Res Rev. 2008. PMID: 17662459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phenone, Hydroxybenzophenone, and Branched Phenone ER Binding and Vitellogenin Agonism in Rainbow Trout In Vitro Models.Appl In Vitro Toxicol. 2019 Mar 13;5(1):62-74. doi: 10.1089/aivt.2018.0008. Appl In Vitro Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 39229248 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen Receptors: A New Frontier in Alzheimer's Disease Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 21;25(16):9077. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169077. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ontogeny of nuclear estrogen receptor isoform expression and the effect of 17beta-estradiol in embryonic rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Feb 5;315(1-2):277-81. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.09.032. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19818378 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and molecular characterization of Rem2 isoforms in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Tissue and central nervous system expression.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 Feb;161(2):93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2011.09.011. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 21983188 Free PMC article.
-
Variation among rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) estrogen receptor isoform 3' untranslated regions and the effect of 17beta-estradiol on mRNA stability in hepatocyte culture.DNA Cell Biol. 2010 May;29(5):229-34. doi: 10.1089/dna.2009.0998. DNA Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20438355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amores A, et al. Zebrafish hox clusters and vertebrate genome evolution. Science. 1994;282:1711–1714. - PubMed
-
- Applied Biosystems. ABI User Bulletin #2. Foster City, CA: 1997.
-
- Ausubel FM, et al. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. John Wiley and Sons, Inc; New York: 1998.
-
- Britt KL, Findlay JK. Estrogen actions in the ovary revisited. J Endocrinol. 2002;175:269–276. - PubMed
-
- Campbell CM, Idler DR. Characterization of an estradiol-induced protein from rainbow trout as vitellogenin by the composition and radioimmunological cross reactivity to ovarian yolk fractions. Biol Reprod. 1980;22:605–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

