Imaging of pulmonary embolism and t-PA therapy effects using MDCT and liposomal iohexol blood pool agent: preliminary results in a rabbit model
- PMID: 17307669
- PMCID: PMC2213908
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2006.12.014
Imaging of pulmonary embolism and t-PA therapy effects using MDCT and liposomal iohexol blood pool agent: preliminary results in a rabbit model
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: Polyethylene glycol-coated liposomal blood pool contrast agents maintain contrast enhancement over several hours. This study aimed to evaluate (long-term) imaging of pulmonary arteries, comparing conventional iodinated contrast with a liposomal blood pool contrast agent. Also, visualization of the (real-time) therapeutic effects of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) on pulmonary embolism (PE) was attempted.
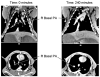
Materials and methods: Six rabbits (weight approximately 4 kg) had autologous blood clots injected through the superior vena cava. Imaging was performed using conventional contrast (iohexol, 350 mg I/ml; GE HealthCare, Princeton, NJ) at a dose of 1400 mg I per animal, and after wash-out, animals were imaged using an iodinated liposomal blood pool agent (88 mg I/mL, dose 900 mg I/animal). Subsequently, five animals were injected with 2 mg of t-PA and imaging continued for up to 4(1/2) hours.
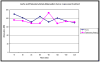
Results: Both contrast agents identified PE in the pulmonary trunk and main pulmonary arteries in all rabbits. Liposomal blood pool agent yielded uniform enhancement, which remained relatively constant throughout the experiments. Conventional agents exhibited nonuniform opacification and rapid clearance postinjection. Three of six rabbits had mistimed bolus injections, requiring repeat injections. Following t-PA, pulmonary embolus volume (central to segmental) decreased in four of five treated rabbits (range 10-57%, mean 42%). One animal showed no response to t-PA.
Conclusions: Liposomal blood pool agents effectively identified acute PE without need for reinjection. PE resolution following t-PA was quantifiable over several hours. Blood pool agents offer the potential for repeated imaging procedures without need for repeated (nephrotoxic) contrast injections.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Long-residence-time nano-scale liposomal iohexol for X-ray-based blood pool imaging.Acad Radiol. 2003 May;10(5):475-83. doi: 10.1016/s1076-6332(03)80055-7. Acad Radiol. 2003. PMID: 12755534
-
Blood pool and liver enhancement in CT with liposomal lodixanol: comparison with lohexol.Acad Radiol. 1999 Mar;6(3):176-83. doi: 10.1016/S1076-6332(99)80404-8. Acad Radiol. 1999. PMID: 10898037
-
Contrast medium injection optimisation in spiral CT for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism.Radiol Med. 2003 May-Jun;105(5-6):416-24. Radiol Med. 2003. PMID: 12949452 English, Italian.
-
Thrombolytic therapy of acute pulmonary embolism: current status and future potential.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 Nov;10(5 Suppl B):96B-104B. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80434-5. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987. PMID: 3117862 Review.
-
High-resolution CT vascular imaging using blood pool contrast agents.Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2012 Jan;8(1):18-22. doi: 10.14797/mdcj-8-1-18. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2012. PMID: 22891106 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rodent models of pulmonary embolism and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension.Heliyon. 2022 Feb 24;8(3):e09014. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09014. eCollection 2022 Mar. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35295664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small, Long Blood Half-Life Iodine Nanoparticle for Vascular and Tumor Imaging.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 14;8(1):13803. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31940-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30218059 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-energy computed tomography imaging of atherosclerotic plaques in a mouse model using a liposomal-iodine nanoparticle contrast agent.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Mar 1;6(2):285-94. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.112.000119. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23349231 Free PMC article.
-
Novel intravascular tantalum oxide-based contrast agent achieves improved vascular contrast enhancement and conspicuity compared to Iopamidol in an animal multiphase CT protocol.Eur Radiol Exp. 2024 Oct 4;8(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s41747-024-00509-2. Eur Radiol Exp. 2024. PMID: 39365418 Free PMC article.
-
X-ray-computed tomography contrast agents.Chem Rev. 2013 Mar 13;113(3):1641-66. doi: 10.1021/cr200358s. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Chem Rev. 2013. PMID: 23210836 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- ESC Task Force on Pulmonary Embolism. Guidelines on management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2000;21:1301–1336. - PubMed
-
- O’Neill JM, Wright L, Murchison JT. Helical CTPA in the investigation of pulmonary embolism: a 6-year review. Clin Radiol. 2004;59:819–825. - PubMed
-
- Wittram C, Meehan MJ, Halpern EF, Shepard JA, McLoud TC, Thrall JH. Trends in thoracic radiology over a decade at a large academic medical center. J Thorac Imaging. 2004;19:164–170. - PubMed
-
- Le Gal G, Bounameaux H. Diagnosing pulmonary embolism: running after the decreasing prevalence of cases among suspected patients. J Thromb Haemost. 2004;2:1244–1246. [editorial] - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

