Lipolytic enzymes in Myxococcus xanthus
- PMID: 17307851
- PMCID: PMC1855839
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01772-06
Lipolytic enzymes in Myxococcus xanthus
Abstract
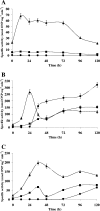
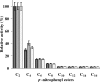
The genome of Myxococcus xanthus encodes lipolytic enzymes in three different families: patatin lipases, alpha/beta hydrolases, and GDSL lipases. One member of each family was characterized. The protein encoded by MXAN_3852 contains motifs characteristic of patatins. MXAN_5522 encodes a protein with the G-X-S-X-G motif characteristic of the lipase subfamily of alpha/beta hydrolases. MXAN_4569 encodes a member of the GDSL family of lipolytic enzymes. Strains with deletions of MXAN_5522 and MXAN_4569 undergo faster development and earlier myxospore formation than the wild-type strain. The MXAN_5522 mutation results in spore yields substantially higher than those seen for wild-type cells. Gene expression analysis using translational lacZ fusions indicates that while all three genes are expressed during development, only MXAN_5522 and MXAN_4569 are expressed during vegetative growth. The proteins encoded by these genes were overexpressed using a T7 RNA polymerase transcription (pET102/D-TOPO) system in Escherichia coli BL21 Star (DE3) cells. The substrate specificities of the purified enzymes were investigated using p-nitrophenyl esters with chain lengths from C(2) to C(16). These enzymes preferentially hydrolyzed esters of short-chain fatty acids, yielding the highest activity with p-nitrophenyl acetate.
Figures
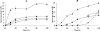
Similar articles
-
Molecular cloning of a novel bioH gene from an environmental metagenome encoding a carboxylesterase with exceptional tolerance to organic solvents.BMC Biotechnol. 2013 Feb 15;13:13. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-13-13. BMC Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23413993 Free PMC article.
-
Two PAAR Proteins with Different C-Terminal Extended Domains Have Distinct Ecological Functions in Myxococcus xanthus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Apr 13;87(9):e00080-21. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00080-21. Print 2021 Apr 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33608292 Free PMC article.
-
The cold-active Lip1 lipase from the Antarctic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 is a member of a new bacterial lipolytic enzyme family.Extremophiles. 2008 May;12(3):311-23. doi: 10.1007/s00792-008-0163-9. Epub 2008 Apr 24. Extremophiles. 2008. PMID: 18437283
-
Eukaryotic-like protein serine/threonine kinases in Myxococcus xanthus, a developmental bacterium exhibiting social behavior.J Cell Biochem. 1993 Jan;51(1):29-33. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240510107. J Cell Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8432741 Review.
-
GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases.Prog Lipid Res. 2004 Nov;43(6):534-52. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2004.09.002. Prog Lipid Res. 2004. PMID: 15522763 Review.
Cited by
-
Myxococcus xanthus R31 Suppresses Tomato Bacterial Wilt by Inhibiting the Pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum With Secreted Proteins.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 7;12:801091. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.801091. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35197943 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acids from membrane lipids become incorporated into lipid bodies during Myxococcus xanthus differentiation.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 6;9(6):e99622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099622. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24906161 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-cell transfer of adaptation traits benefits kin and actor in a cooperative microbe.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 23;121(30):e2402559121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2402559121. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39012831 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty Acid Oxidation Is Required for Myxococcus xanthus Development.J Bacteriol. 2018 Apr 24;200(10):e00572-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00572-17. Print 2018 May 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29507089 Free PMC article.
-
A Lipase Gene of Thermomyces lanuginosus: Sequence Analysis and High-Efficiency Expression in Pichia pastoris.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 29;25(21):11591. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111591. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akoh, C. C., G. C. Lee, Y. C. Liaw, T. H. Huang, and J. F. Shaw. 2004. GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog. Lipid Res. 43:534-552. - PubMed
-
- Anthonsen, H. W., A. Baptista, F. Drablos, P. Martel, S. B. Petersen, M. Sebastiao, and L. Vaz. 1995. Lipases and esterases: a review of their sequences, structure and evolution. Biotechnol. Annu. Rev. 1:315-371. - PubMed
-
- Banerji, S., and A. Flieger. 2004. Patatin-like proteins: a new family of lipolytic enzymes present in bacteria? Microbiology 150:522-525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

