Multiple roles of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 in plant cells include spatially regulated recruitment of coatomer and elements of the Golgi matrix
- PMID: 17307898
- PMCID: PMC1851833
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.094953
Multiple roles of ADP-ribosylation factor 1 in plant cells include spatially regulated recruitment of coatomer and elements of the Golgi matrix
Abstract
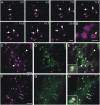
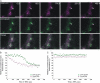
Recent evidence indicates that ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1) carries out multiple roles in plant cells that may be independent from the established effector complex COPI. To investigate potential COPI-independent functions, we have followed the dynamics of ARF1 and a novel putative effector, the plant golgin GRIP-related ARF-binding domain-containing Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) protein 1 (GDAP1) in living plant cells. We present data that ascribe a new role to ARF1 in plant cell membrane traffic by showing that the GTPase functions to recruit GDAP1 to membranes. In addition, although ARF1 appears to be central to the recruitment of both COPI components and the golgin, we have established a different subcellular distribution of these ARF1 effectors. Live cell imaging demonstrates that GDAP1 and COPI are distributed on Golgi membranes. However, GDAP1 is also found on ARF1-labeled structures that lack coatomer, suggesting that the membrane environment, rather than ARF1 alone, influences the differential recruitment of ARF1 effectors. In support of this hypothesis, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching analyses demonstrated that GDAP1 and COPI have different kinetics on membranes during the cycle of activation and inactivation of ARF1. Therefore, our data support a model where modulation of the cellular functions of ARF1 in plant cells encompasses not only the intrinsic activities of the effectors, but also differential recruitment onto membranes that is spatially regulated.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Correct targeting of plant ARF GTPases relies on distinct protein domains.Traffic. 2008 Jan;9(1):103-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00671.x. Epub 2007 Nov 27. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 17988226
-
In tobacco leaf epidermal cells, the integrity of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum and of ER export sites depends on active COPI machinery.Plant J. 2006 Apr;46(1):95-110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02675.x. Plant J. 2006. PMID: 16553898
-
Dissection of COPI and Arf1 dynamics in vivo and role in Golgi membrane transport.Nature. 2002 May 9;417(6885):187-93. doi: 10.1038/417187a. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12000962
-
Building a secretory apparatus: role of ARF1/COPI in Golgi biogenesis and maintenance.Histochem Cell Biol. 1998 May-Jun;109(5-6):449-62. doi: 10.1007/s004180050247. Histochem Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9681627 Review.
-
The COPI system: molecular mechanisms and function.FEBS Lett. 2009 Sep 3;583(17):2701-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.07.032. Epub 2009 Jul 22. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19631211 Review.
Cited by
-
BEX1/ARF1A1C is required for BFA-sensitive recycling of PIN auxin transporters and auxin-mediated development in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Physiol. 2014 Apr;55(4):737-49. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct196. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24369434 Free PMC article.
-
The Coordinated KNR6-AGAP-ARF1 Complex Modulates Vegetative and Reproductive Traits by Participating in Vesicle Trafficking in Maize.Cells. 2021 Sep 30;10(10):2601. doi: 10.3390/cells10102601. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685581 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Lipidomics and Proteomics of Lipid Droplets in the Mesocarp and Seed Tissues of Chinese Tallow (Triadica sebifera).Front Plant Sci. 2017 Aug 2;8:1339. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01339. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28824675 Free PMC article.
-
Sweet control: intracellular sorting of glycoproteins in plants.J Exp Bot. 2025 May 27;76(8):2035-2038. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraf095. J Exp Bot. 2025. PMID: 40425529 Free PMC article.
-
The secretory system of Arabidopsis.Arabidopsis Book. 2008;6:e0116. doi: 10.1199/tab.0116. Epub 2008 Sep 30. Arabidopsis Book. 2008. PMID: 22303241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boevink P, Oparka K, Santa Cruz S, Martin B, Betteridge A, Hawes C (1998) Stacks on tracks: the plant Golgi apparatus traffics on an actin/ER network. Plant J 15 441–447 - PubMed
-
- Bolte S, Talbot C, Boutte Y, Catrice O, Read ND, Satiat-Jeunemaitre B (2004) FM-dyes as experimental probes for dissecting vesicle trafficking in living plant cells. J Microsc 214 159–173 - PubMed
-
- Contreras I, Ortiz-Zapater E, Aniento F (2004) Sorting signals in the cytosolic tail of membrane proteins involved in the interaction with plant ARF1 and coatomer. Plant J 38 685–698 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

