Tapetosomes in Brassica tapetum accumulate endoplasmic reticulum-derived flavonoids and alkanes for delivery to the pollen surface
- PMID: 17307923
- PMCID: PMC1867322
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.049049
Tapetosomes in Brassica tapetum accumulate endoplasmic reticulum-derived flavonoids and alkanes for delivery to the pollen surface
Abstract
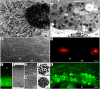
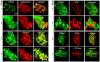
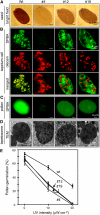
Tapetosomes are abundant organelles in tapetum cells during the active stage of pollen maturation in Brassicaceae species. They possess endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-derived vesicles and oleosin-coated lipid droplets, but their overall composition and function have not been established. In situ localization analyses of developing Brassica napus anthers revealed flavonoids present exclusively in tapetum cells, first in an ER network along with flavonoid-3'-hydroxylase and then in ER-derived tapetosomes. Flavonoids were absent in the cytosol, elaioplasts, vacuoles, and nuclei. Subcellular fractionation of developing anthers localized both flavonoids and alkanes in tapetosomes. Subtapetosome fractionation localized flavonoids in ER-derived vesicles, and alkanes and oleosins in lipid droplets. After tapetum cell death, flavonoids, alkanes, and oleosins were located on mature pollen. In the Arabidopsis thaliana mutants tt12 and tt19 devoid of a flavonoid transporter, flavonoids were present in the cytosol in reduced amounts but absent in tapetosomes and were subsequently located on mature pollen. tt4, tt12, and tt19 pollen was more susceptible than wild-type pollen to UV-B irradiation on subsequent germination. Thus, tapetosomes accumulate ER-derived flavonoids, alkanes, and oleosins for discharge to the pollen surface upon cell death. This tapetosome-originated pollen coat protects the haploidic pollen from UV light damage and water loss and aids water uptake.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tapetal oleosins play an essential role in tapetosome formation and protein relocation to the pollen coat.New Phytol. 2016 Jan;209(2):691-704. doi: 10.1111/nph.13611. Epub 2015 Aug 25. New Phytol. 2016. PMID: 26305561
-
Lipid-rich tapetosomes in Brassica tapetum are composed of oleosin-coated oil droplets and vesicles, both assembled in and then detached from the endoplasmic reticulum.Plant J. 2005 Sep;43(6):889-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02502.x. Plant J. 2005. PMID: 16146527
-
The maize tapetum employs diverse mechanisms to synthesize and store proteins and flavonoids and transfer them to the pollen surface.Plant Physiol. 2012 Apr;158(4):1548-61. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.189241. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22291199 Free PMC article.
-
Development and disintegration of tapetum-specific lipid-accumulating organelles, elaioplasts and tapetosomes, in Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus.Plant Sci. 2013 Jun;207:25-36. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.02.008. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23602096
-
Constituents of the tapetosomes and elaioplasts in Brassica campestris tapetum and their degradation and retention during microsporogenesis.Plant J. 1998 Dec;16(5):541-51. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00325.x. Plant J. 1998. PMID: 10036772
Cited by
-
The transcription factors and pathways underpinning male reproductive development in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Feb 8;15:1354418. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1354418. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38390292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of CCoAOMT1 and COMT1 in Arabidopsis anthers.Planta. 2012 Jul;236(1):51-61. doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1586-6. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Planta. 2012. PMID: 22258746
-
Characterization of a new class of blue-fluorescent lipid droplet markers for live-cell imaging in plants.Plant Cell Rep. 2015 Apr;34(4):655-65. doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1738-4. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Plant Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25604989
-
Biochemistry and Molecular Basis of Intracellular Flavonoid Transport in Plants.Plants (Basel). 2022 Apr 1;11(7):963. doi: 10.3390/plants11070963. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dose effects of restorer gene modulate pollen fertility in cotton CMS-D2 restorer lines via auxin signaling and flavonoid biosynthesis.Plant Cell Rep. 2023 Nov;42(11):1705-1719. doi: 10.1007/s00299-023-03053-2. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Plant Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37715064
References
-
- Bewley, J.D., Hempel, F.D., McCormick, S., and Zambryski, P. (2000). Reproductive development. In Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants, B.B. Buchanan, W. Gruissem, and R.L. Jones, eds (Rockville, MD: American Society of Plant Physiologists), pp. 988–1043.
-
- Bih, F.Y., Wu, S.S.H., Ratnayake, C., Walling, L.L., Nothnagel, E.A., and Huang, A.H.C. (1999). The predominant protein on the surface of maize pollen is an endoxylanase synthesized by a tapetum mRNA with a long 5′ leader. J. Biol. Chem. 32 22884–22894. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

