Priming with an adenovirus 35-circumsporozoite protein (CS) vaccine followed by RTS,S/AS01B boosting significantly improves immunogenicity to Plasmodium falciparum CS compared to that with either malaria vaccine alone
- PMID: 17307942
- PMCID: PMC1865796
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01879-06
Priming with an adenovirus 35-circumsporozoite protein (CS) vaccine followed by RTS,S/AS01B boosting significantly improves immunogenicity to Plasmodium falciparum CS compared to that with either malaria vaccine alone
Abstract
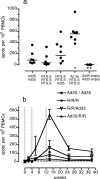
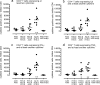
The RTS,S/AS02A protein-based vaccine consistently demonstrates significant protection against infection with Plasmodium falciparum malaria and also against clinical malaria and severe disease in children in areas of endemicity. Here we demonstrate with rhesus macaques that priming with a replication-defective human adenovirus serotype 35 (Ad35) vector encoding circumsporozoite protein (CS) (Ad35.CS), followed by boosting with RTS,S in an improved MPL- and QS21-based adjuvant formulation, AS01B, maintains antibody responses and dramatically increases levels of T cells producing gamma interferon and other Th1 cytokines in response to CS peptides. The increased T-cell responses induced by the combination of Ad35.CS and RTS,S/AS01B are sustained for at least 6 months postvaccination and may translate to improved and more durable protection against P. falciparum infection in humans.
Figures

References
-
- Alonso, P., J. Sacarlal, J. Aponte, A. Leach, E. Macete, P. Aide, B. Sigauque, J. Milman, I. Mandomando, Q. Bassat, C. Guinovart, M. Espasa, S. Corachan, M. Lievens, M. Navia, M. Dubois, C. Menendez, F. Dubovsky, J. Cohen, R. Thompson, and W. Ballou. 2005. Duration of protection with RTS,S/AS02A malaria vaccine in prevention of Plasmodium falciparum disease in Mozambican children: single-blind extended follow-up of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 366:2012-2018. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, P. L., J. Sacarlal, J. J. Aponte, A. Leach, E. Macete, J. Milman, I. Mandomando, B. Spiessens, C. Guinovart, M. Espasa, Q. Bassat, P. Aide, O. Ofori-Anyinam, M. M. Navia, S. Corachan, M. Ceuppens, M. C. Dubois, M. A. Demoitie, F. Dubovsky, C. Menendez, N. Tornieporth, W. R. Ballou, R. Thompson, and J. Cohen. 2004. Efficacy of the RTS,S/AS02A vaccine against Plasmodium falciparum infection and disease in young African children: randomised controlled trial. Lancet 364:1411-1420. - PubMed
-
- Barouch, D. H., and G. J. Nabel. 2005. Adenovirus vector-based vaccines for human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Hum. Gene Ther. 16:149-156. - PubMed
-
- Boyson, J. E., C. Shufflebotham, L. F. Cadavid, J. A. Urvater, L. A. Knapp, A. L. Hughes, and D. I. Watkins. 1996. The MHC class I genes of the rhesus monkey. Different evolutionary histories of MHC class I and II genes in primates. J. Immunol. 156:4656-4665. - PubMed
-
- Bruna-Romero, O., G. Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza, J. C. Hafalla, M. Tsuji, and R. S. Nussenzweig. 2001. Complete, long-lasting protection against malaria of mice primed and boosted with two distinct viral vectors expressing the same plasmodial antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:11491-11496. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

