A mariner-based transposition system for Listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 17308180
- PMCID: PMC1855599
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02844-06
A mariner-based transposition system for Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
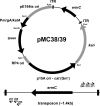
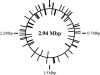
In this study, we developed a new mariner-based transposition system for Listeria monocytogenes. The mariner-based system has a high rate of transposition and a low rate of plasmid retention, and transposition is very random, making it an ideal tool for high-throughput transposon mutagenesis in L. monocytogenes.
Figures
References
-
- Bishop, D. K., and D. J. Hinrichs. 1987. Adoptive transfer of immunity to Listeria monocytogenes: the influence of in vitro stimulation on lymphocyte subset requirements. J. Immunol. 139:2005-2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

