Outbreak of an acute aflatoxicosis in Kenya in 2004: identification of the causal agent
- PMID: 17308181
- PMCID: PMC1855601
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02370-06
Outbreak of an acute aflatoxicosis in Kenya in 2004: identification of the causal agent
Abstract
Maize contaminated with aflatoxins has been implicated in deadly epidemics in Kenya three times since 1981, but the fungi contaminating the maize with aflatoxins have not been characterized. Here we associate the S strain of Aspergillus flavus with lethal aflatoxicoses that took more than 125 lives in 2004.
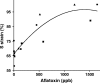
Figures
References
-
- Azziz-Baumgartner, E., K. Lindblade, K. Gieseker, H. Schurz Rogers, S. Kieszak, H. Njapau, R. Schleicher, L. F. McCoy, A. Misore, K. DeCock, C. Rubin, L. Slutsker, and the Aflatoxin Investigative Group. 2005. Case-control study of an acute aflatoxicosis outbreak, Kenya, 2004. Environ. Health Perspect. 113:1779-1783. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay, R., S. Kiewnick, J. Atehnkeng, M. Donner, P. J. Cotty, and K. Hell. 2005. Biological control of aflatoxin contamination in maize in Africa, p. 66. Abstr. Tropentag 2005 Conf. Int. Agric. Res. Dev. Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich, Switzerland.
-
- Bankole, S. A., and A. Adebanjo. 2003. Mycotoxins in food in West Africa: current situation and possibilities of controlling it. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2:254-263.
-
- Brown, R. L., P. J. Cotty, T. E. Cleveland, and N. W. Widstrom. 1993. The living embryo influences accumulation of aflatoxin in maize kernels. J. Food Prot. 56:967-971. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

