Synthesis and properties of size-expanded DNAs: toward designed, functional genetic systems
- PMID: 17309194
- PMCID: PMC2539066
- DOI: 10.1021/ar068200o
Synthesis and properties of size-expanded DNAs: toward designed, functional genetic systems
Abstract
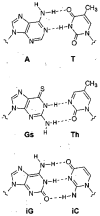
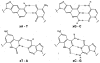
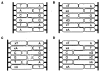
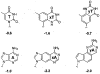
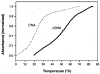
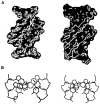
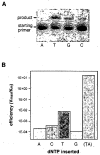
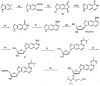
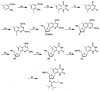
We describe the design, synthesis, and properties of DNA-like molecules in which the base pairs are expanded by benzo homologation. The resulting size-expanded genetic helices are called xDNA ("expanded DNA") and yDNA ("wide DNA"). The large component bases are fluorescent, and they display high stacking affinity. When singly substituted into natural DNA, they are destabilizing because the benzo-expanded base pair size is too large for the natural helix. However, when all base pairs are expanded, xDNA and yDNA form highly stable, sequence-selective double helices. The size-expanded DNAs are candidates for components of new, functioning genetic systems. In addition, the fluorescence of expanded DNA bases makes them potentially useful in probing nucleic acids.
Figures


References
-
- McLaughlin LW, Wilson M, Ha SB. Use of Nucleoside Analogues to Probe Biochemical Processes. In: Barton D, Nakanishi K, editors. Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry. Elsevier; Oxford, UK: 1999. pp. 251–284.
-
- Kool ET, Morales JC, Guckian KM. Mimicking the Structures and Functions of DNA: Insights into DNA Stability and Replication. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2000;39:990–1009. - PubMed
-
- Henry AA, Romesberg FE, Beyond ACGT. Augmenting Nature’s Alphabet. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2003;7:727–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

