The gene encoding the splicing factor SF2/ASF is a proto-oncogene
- PMID: 17310252
- PMCID: PMC4595851
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb1209
The gene encoding the splicing factor SF2/ASF is a proto-oncogene
Abstract
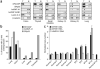
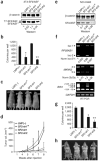
Alternative splicing modulates the expression of many oncogene and tumor-suppressor isoforms. We have tested whether some alternative splicing factors are involved in cancer. We found that the splicing factor SF2/ASF is upregulated in various human tumors, in part due to amplification of its gene, SFRS1. Moreover, slight overexpression of SF2/ASF is sufficient to transform immortal rodent fibroblasts, which form sarcomas in nude mice. We further show that SF2/ASF controls alternative splicing of the tumor suppressor BIN1 and the kinases MNK2 and S6K1. The resulting BIN1 isoforms lack tumor-suppressor activity; an isoform of MNK2 promotes MAP kinase-independent eIF4E phosphorylation; and an unusual oncogenic isoform of S6K1 recapitulates the transforming activity of SF2/ASF. Knockdown of either SF2/ASF or isoform-2 of S6K1 is sufficient to reverse transformation caused by the overexpression of SF2/ASF in vitro and in vivo. Thus, SF2/ASF can act as an oncoprotein and is a potential target for cancer therapy.
Figures
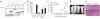
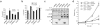
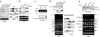
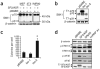


Comment in
-
Splicing oncogenes.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Mar;14(3):174-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb0307-174. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17334403 No abstract available.
References
-
- Johnson JM, et al. Genome-wide survey of human alternative pre-mRNA splicing with exon junction microarrays. Science. 2003;302:2141–2144. - PubMed
-
- Black DL. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:291–336. - PubMed
-
- Mayeda A, Krainer AR. Regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing by hnRNP A1 and splicing factor SF2. Cell. 1992;68:365–375. - PubMed
-
- Cáceres JF, Stamm S, Helfman DM, Krainer AR. Regulation of alternative splicing in vivo by overexpression of antagonistic splicing factors. Science. 1994;265:1706–1709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

