Interleukin-2 enhances CD4+ T cell memory by promoting the generation of IL-7R alpha-expressing cells
- PMID: 17312008
- PMCID: PMC2137906
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20062381
Interleukin-2 enhances CD4+ T cell memory by promoting the generation of IL-7R alpha-expressing cells
Abstract
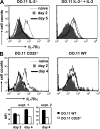
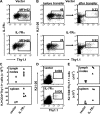
The common gamma chain cytokines interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-7 are important regulators of T cell homeostasis. Although IL-2 is implicated in the acute phase of the T cell response, IL-7 is important for memory T cell survival. We asked whether regulated responsiveness to these growth factors is determined by temporal expression of the cytokine-specific IL-2 receptor (R) alpha and IL-7Ralpha chains. We demonstrate that IL-2Ralpha is expressed early after priming in T cell receptor-transgenic CD4(+) T cells, whereas IL-7Ralpha expression is lost. In the later stage of the response, IL-7Ralpha is reexpressed while IL-2Ralpha expression is silenced. This reciprocal pattern of IL-2Ralpha/IL-7Ralpha expression is disturbed when CD4(+) T cells are primed in the absence of IL-2 signals. Primed IL-2(-/-) or CD25(-/-) (IL-2Ralpha(-/-)) CD4(+) T cells, despite showing normal induction of activation markers and cell division, fail to reexpress IL-7Ralpha late in the response. Because the generation of CD4(+) memory T cells is dependent on IL-7-IL-7Ralpha interactions, primed IL-2(-/-) or CD25(-/-) CD4(+) T cells develop poorly into long-lived memory cells. Retrovirus-mediated expression of IL-7Ralpha in IL-2(-/-) T cells restores their capacity for long-term survival. These results identify IL-2 as a factor regulating IL-7Ralpha expression and, consequently, memory T cell homeostasis in vivo.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Upregulated IL-7 receptor α expression on colitogenic memory CD4+ T cells may participate in the development and persistence of chronic colitis.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 15;186(4):2623-32. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000057. Epub 2011 Jan 7. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21217010
-
Impaired CD8 T cell memory and CD4 T cell primary responses in IL-7R alpha mutant mice.J Exp Med. 2007 Mar 19;204(3):619-31. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061871. Epub 2007 Feb 26. J Exp Med. 2007. PMID: 17325202 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive expression of IL-7 receptor alpha does not support increased expansion or prevent contraction of antigen-specific CD4 or CD8 T cells following Listeria monocytogenes infection.J Immunol. 2008 Mar 1;180(5):2855-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.5.2855. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18292507
-
IL-1β strikingly enhances antigen-driven CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2013;78:117-24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2013.78.021246. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2013. PMID: 24092469 Review.
-
Cytokine control of memory T-cell development and survival.Nat Rev Immunol. 2003 Apr;3(4):269-79. doi: 10.1038/nri1052. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12669018 Review.
Cited by
-
The microRNA miR-182 is induced by IL-2 and promotes clonal expansion of activated helper T lymphocytes.Nat Immunol. 2010 Nov;11(11):1057-62. doi: 10.1038/ni.1945. Epub 2010 Oct 10. Nat Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20935646
-
SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination-induced immunological memory in human nonlymphoid and lymphoid tissues.J Clin Invest. 2023 Dec 15;133(24):e171797. doi: 10.1172/JCI171797. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37815874 Free PMC article.
-
Partial STAT5 signaling is sufficient for CD4+ T cell priming but not memory formation.Cytokine. 2022 Feb;150:155770. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155770. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Cytokine. 2022. PMID: 34839177 Free PMC article.
-
Early programming and late-acting checkpoints governing the development of CD4 T-cell memory.Immunology. 2018 Sep;155(1):53-62. doi: 10.1111/imm.12942. Epub 2018 May 21. Immunology. 2018. PMID: 29701246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interleukin 23 receptor is essential for the terminal differentiation of interleukin 17-producing effector T helper cells in vivo.Nat Immunol. 2009 Mar;10(3):314-24. doi: 10.1038/ni.1698. Epub 2009 Feb 1. Nat Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19182808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Stipdonk, M.J., E.E. Lemmens, and S.P. Schoenberger. 2001. Naive CTLs require a single brief period of antigenic stimulation for clonal expansion and differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2:423–429. - PubMed
-
- Lau, L.L., B.D. Jamieson, T. Somasundaram, and R. Ahmed. 1994. Cytotoxic T-cell memory without antigen. Nature. 369:648–652. - PubMed
-
- Murali-Krishna, K., L.L. Lau, S. Sambhara, F. Lemonnier, J. Altman, and R. Ahmed. 1999. Persistence of memory CD8 T cells in MHC class I-deficient mice. Science. 286:1377–1381. - PubMed
-
- Bourgeois, C., B. Rocha, and C. Tanchot. 2002. A role for CD40 expression on CD8+ T cells in the generation of CD8+ T cell memory. Science. 297:2060–2063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

