Murine neonatal CD4+ cells are poised for rapid Th2 effector-like function
- PMID: 17312108
- PMCID: PMC2112939
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.5.2667
Murine neonatal CD4+ cells are poised for rapid Th2 effector-like function
Abstract
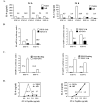
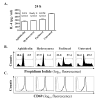
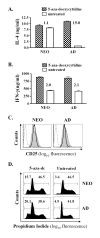
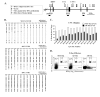
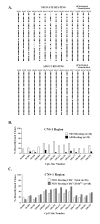
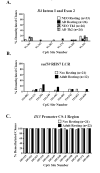
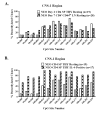
Murine neonates typically mount Th2-biased immune responses. This entails a cell-intrinsic component whose molecular basis is unknown. We found that neonatal CD4(+) T cells are uniquely poised for rapid Th2 function. Within 24 h of activation, neonatal CD4(+) cells made high levels of IL-4 and IL-13 mRNA and protein. The rapid high-level IL-4 production arose from a small subpopulation of cells, did not require cell cycle entry, and was unaffected by pharmacologic DNA demethylation. CpG methylation analyses in resting neonatal cells revealed pre-existing hypomethylation at a key Th2 cytokine regulatory region, termed conserved noncoding sequence 1 (CNS-1). Robust Th2 function and increased CNS-1 demethylation was a stable property that persisted in neonatal Th2 effectors. The transcription factor STAT6 was not required for CNS-1 demethylation and this state was already established in neonatal CD4 single-positive thymocytes. CNS-1 demethylation levels were much greater in IL-4-expressing CD4 single-positive thymocytes compared with unactivated cells. Together, these results indicate that neonatal CD4+ T cells possess distinct qualities that could predispose them toward rapid, effector-like Th2 function.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Single cell analysis reveals that IL-4 receptor/Stat6 signaling is not required for the in vivo or in vitro development of CD4+ lymphocytes with a Th2 cytokine profile.J Immunol. 2000 Mar 15;164(6):3047-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.6.3047. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10706693
-
DNA methylation changes at human Th2 cytokine genes coincide with DNase I hypersensitive site formation during CD4(+) T cell differentiation.J Immunol. 2002 Aug 15;169(4):1893-903. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.4.1893. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12165514
-
Stat6 is necessary and sufficient for IL-4's role in Th2 differentiation and cell expansion.J Immunol. 2001 Jun 15;166(12):7276-81. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.12.7276. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11390477
-
Differential requirements for IL-4/STAT6 signalling in CD4 T-cell fate determination and Th2-immune effector responses.Immunol Cell Biol. 2010 Mar-Apr;88(3):240-3. doi: 10.1038/icb.2009.101. Epub 2009 Dec 15. Immunol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20010912 Review.
-
Maturation of human neonatal CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes into Th1/Th2 effectors.Vaccine. 1998 Aug-Sep;16(14-15):1415-9. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(98)00101-7. Vaccine. 1998. PMID: 9711781 Review.
Cited by
-
CpG-induced Th1-type response in the downmodulation of early development of allergy and inhibition of B7 expression on T cells of newborn mice.J Clin Immunol. 2010 Mar;30(2):280-91. doi: 10.1007/s10875-009-9358-9. Epub 2010 Jan 19. J Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20084440
-
Tissue compartmentalization of T cell responses during early life.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Nov;39(6):593-604. doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0648-7. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 28894935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune vulnerability of infants to tuberculosis.Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:781320. doi: 10.1155/2013/781320. Epub 2013 May 13. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23762096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allergen Exposure in Murine Neonates Promoted the Development of Asthmatic Lungs.Biomedicines. 2021 Jun 18;9(6):688. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060688. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34207237 Free PMC article.
-
A Genetic Model Reveals Biological Features of Neonatal CD4 Helper Cells Undergone Homeostasis in Mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 11;9:659744. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.659744. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33777965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adkins B, Leclerc C, Marshall-Clarke S. Neonatal adaptive immunity comes of age. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:553–564. - PubMed
-
- Adkins B, Hamilton K. Freshly isolated, murine neonatal T cells produce IL-4 in response to anti-CD3 stimulation. J Immunol. 1992;149:3448–3455. - PubMed
-
- Adkins B, Bu Y, Guevara P. Murine neonatal CD4+ lymph node cells are highly deficient in the development of antigen-specific Th1 function in adoptive adult hosts. J Immunol. 2002;169:4998–5004. - PubMed
-
- Ansel KM, Lee DU, Rao A. An epigenetic view of helper T cell differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:616–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

