Expression profile of FcgammaRIIb on leukocytes and its dysregulation in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 17312177
- PMCID: PMC2824439
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.5.3272
Expression profile of FcgammaRIIb on leukocytes and its dysregulation in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
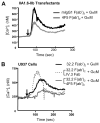
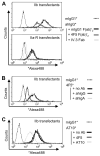
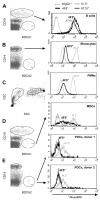
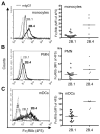
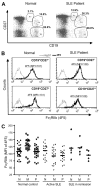
FcgammaRIIb (CD32B, Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man 604590), an IgG FcR with a tyrosine-based inhibitory motif, plays a critical role in the balance of tolerance and autoimmunity in murine models. However, the high degree of homology between FcgammaRIIb and FcgammaRIIa in humans and the lack of specific Abs to differentiate them have hampered study of the normal expression profile of FcgammaRIIb and its potential dysregulation in autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Using our newly developed anti-FcgammaRIIb mAb 4F5 which does not react with FcgammaRIIa, we found that FcgammaRIIb is expressed on the cell surface of circulating B lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, myeloid dendritic cells (DCs), and at very low levels on plasmacytoid DCs from some donors. Normal donors with the less frequent 2B.4 promoter haplotype have higher FcgammaRIIb expression on monocytes, neutrophils, and myeloid DCs similar to that reported for B lymphocytes, indicating that FcgammaRIIb expression on both myeloid and lymphoid cells is regulated by the naturally occurring regulatory single nucleotide polymorphisms in the FCGR2B promoter. FcgammaRIIb expression in normal controls is up-regulated on memory B lymphocytes compared with naive B lymphocytes. In contrast, in active SLE, FcgammaRIIb is significantly down-regulated on both memory and plasma B lymphocytes compared with naive and memory/plasma B lymphocytes from normals. Similar down-regulation of FcgammaRIIb on myeloid-lineage cells in SLE was not seen. Our studies demonstrate the constitutive regulation of FcgammaRIIb by natural gene polymorphisms and the acquired dysregulation in SLE autoimmunity, which may identify opportunities for using this receptor as a therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Daeron M. Fc receptor biology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:203–234. - PubMed
-
- Ravetch JV, Bolland S. IgG Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:275–290. - PubMed
-
- Amigorena S, Bonnerot C, Drake JR, Choquet D, Hunziker W, Guillet JG, Webster P, Sautes C, Mellman I, Fridman WH. Cytoplasmic domain heterogeneity and functions of IgG Fc receptors in B lymphocytes. Science. 1992;256:1808–1812. - PubMed
-
- Ono M, Bolland S, Tempst P, Ravetch JV. Role of the inositol phosphatase SHIP in negative regulation of the immune system by the receptor FcγRIIB. Nature. 1996;383:263–266. - PubMed
-
- Hunter S, Indik ZK, Kim MK, Cauley MD, Park JG, Schreiber AD. Inhibition of Fcγ receptor-mediated phagocytosis by a nonphagocytic Fcγ receptor. Blood. 1998;91:1762–1768. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR042476/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR 33062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR 00032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR033062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR054530/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR 49084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR 48311/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR 42476/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI040068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR048311/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI 40068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

