The N-terminus of Dictyostelium Scar interacts with Abi and HSPC300 and is essential for proper regulation and function
- PMID: 17314411
- PMCID: PMC1855017
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-06-0518
The N-terminus of Dictyostelium Scar interacts with Abi and HSPC300 and is essential for proper regulation and function
Abstract
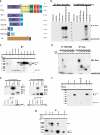
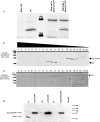
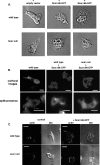
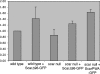
Scar/WAVE proteins, members of the conserved Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) family, promote actin polymerization by activating the Arp2/3 complex. A number of proteins, including a complex containing Nap1, PIR121, Abi1/2, and HSPC300, interact with Scar/WAVE, though the role of this complex in regulating Scar function remains unclear. Here we identify a short N-terminal region of Dictyostelium Scar that is necessary and sufficient for interaction with HSPC300 and Abi in vitro. Cells expressing Scar lacking this N-terminal region show abnormalities in F-actin distribution, cell morphology, movement, and cytokinesis. This is true even in the presence of wild-type Scar. The data suggest that the first 96 amino acids of Scar are necessary for participation in a large-molecular-weight protein complex, and that this Scar-containing complex is responsible for the proper localization and regulation of Scar. The presence of mis-regulated or unregulated Scar has significant deleterious effects on cells and may explain the need to keep Scar activity tightly controlled in vivo either by assembly in a complex or by rapid degradation.
Figures

References
-
- Baba Y., et al. Involvement of wiskott-aldrich syndrome protein in B-cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase pathway. Blood. 1999;93:2003–2012. - PubMed
-
- Bear J. E. Atlanta, GA: Emory University; 1998. SCAR Defines a New Family of WASP-related Actin Cytoskeleton Regulators.
-
- Blagg S. L., Stewart M., Sambles C., Insall R. H. PIR121 regulates pseudopod dynamics and SCAR activity in Dictyostelium. Curr. Biol. 2003a;13:1480–1487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

