The Homer family proteins
- PMID: 17316461
- PMCID: PMC1852408
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-2-206
The Homer family proteins
Abstract
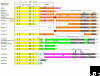
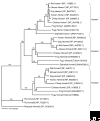
The Homer family of adaptor proteins consists of three members in mammals, and homologs are also known in other animals but not elsewhere. They are predominantly localized at the postsynaptic density in mammalian neurons and act as adaptor proteins for many postsynaptic density proteins. As a result of alternative splicing each member has several variants, which are classified primarily into the long and short forms. The long Homer forms are constitutively expressed and consist of two major domains: the amino-terminal target-binding domain, which includes an Enabled/vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (Ena/VASP) homology 1 (EVH1) domain, and the carboxy-terminal self-assembly domain containing a coiled-coil structure and leucine zipper motif. Multimers of long Homer proteins, coupled through their carboxy-terminal domains, are thought to form protein clusters with other postsynaptic density proteins, which are bound through the amino-terminal domains. Such Homer-mediated clustering probably regulates or facilitates signal transduction or cross-talk between target proteins. The short Homer forms lack the carboxy-terminal domain; they are expressed in an activity-dependent manner as immediate-early gene products, possibly disrupting Homer clusters by competitive binding to target proteins. Homer proteins are also involved in diverse non-neural physiological functions.
Figures
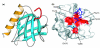

Similar articles
-
Homer regulates the association of group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors with multivalent complexes of homer-related, synaptic proteins.Neuron. 1998 Oct;21(4):707-16. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80588-7. Neuron. 1998. PMID: 9808458
-
Molecular characterisation of two structurally distinct groups of human homers, generated by extensive alternative splicing.J Mol Biol. 2000 Feb 4;295(5):1185-200. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3436. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10653696
-
Involvement of unique leucine-zipper motif of PSD-Zip45 (Homer 1c/vesl-1L) in group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptor clustering.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Nov 23;96(24):13801-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.24.13801. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10570153 Free PMC article.
-
[Scaffold proteins (MAGUK, Shank and Homer) in postsynaptic density in the central nervous system].Postepy Biochem. 2007;53(2):188-97. Postepy Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17969881 Review. Polish.
-
The Homer family and the signal transduction system at glutamatergic postsynaptic density: potential role in behavior and pharmacotherapy.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2003 Summer;37(3):51-83. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2003. PMID: 14608240 Review.
Cited by
-
Homers at the Interface between Reward and Pain.Front Psychiatry. 2013 Jun 7;4:39. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00039. eCollection 2013. Front Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23761764 Free PMC article.
-
Imbalances in prefrontal cortex CC-Homer1 versus CC-Homer2 expression promote cocaine preference.J Neurosci. 2013 May 8;33(19):8101-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1727-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23658151 Free PMC article.
-
A single nucleotide polymorphism in the HOMER1 gene is associated with sleep latency and theta power in sleep electroencephalogram.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 9;15(7):e0223632. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223632. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32645048 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the eukaryotic ARP2/3 activators of the WASP family: WASP, WAVE, WASH, and WHAMM, and the proposed new family members WAWH and WAML.BMC Res Notes. 2012 Feb 8;5:88. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-88. BMC Res Notes. 2012. PMID: 22316129 Free PMC article.
-
The backbone of the post-synaptic density originated in a unicellular ancestor of choanoflagellates and metazoans.BMC Evol Biol. 2010 Feb 3;10:34. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-34. BMC Evol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20128896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xiao B, Tu JC, Petralia RS, Yuan JP, Doan A, Breder CD, Ruggiero A, Lanahan AA, Wenthold RJ, Worley PF. Homer regulates the association of group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors with multivalent complexes of homer-related, synaptic proteins. Neuron. 1998;21:707–716. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80588-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

