[Current management of acute pediatric rhinosinusitis in France]
- PMID: 17317063
- PMCID: PMC7119127
- DOI: 10.1016/j.medmal.2006.11.008
[Current management of acute pediatric rhinosinusitis in France]
Abstract
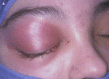
A multidisciplinary panel of specialists and general practitioners provided definitions for the different forms of acute pediatric rhinosinusitis, with a description of the main symptoms and signs. They emphasized the role of concomitant systemic diseases, such as allergy and immunological disorders. Incidence, description, and management of complications are presented. They also provided the indications for radiological examination and microbiological investigations. The adequate medical management, particularly the place and the type of antibiotics, is analyzed and discussed, and guidelines for practical situations are suggested.
Un groupe de médecins généralistes et multidisciplinaire de spécialistes contribue à définir les différentes formes de sinusites ou rhinosinusites aiguës de l'enfant à partir des principaux symptômes et signes cliniques. Le rôle des pathologies associées telles que l'allergie, les troubles immunitaires est envisagé. L'incidence, la présentation clinique et la prise en charge des complications sont présentées. Les indications des examens radiologiques et biologiques sont analysées. La prise en charge médicale en particulier, la place et le type des antibiotiques sont discutés. Des propositions de prise en charge selon des situations cliniques rencontrées en pratique sont présentées.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management of rhinosinusitis in children.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1999 Oct 5;49 Suppl 1:S95-100. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5876(99)00141-x. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1999. PMID: 10577784
-
Chapter 5: Pediatric rhinosinusitis: definitions, diagnosis and management--an overview.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2013 May-Jun;27 Suppl 1:S16-9. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2013.27.3896. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2013. PMID: 23711033 Review.
-
[Diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic rhinosinusitis].MMW Fortschr Med. 2013 Mar 28;155 Spec No 1(1):49-53; quiz 54. doi: 10.1007/s15006-013-0321-6. MMW Fortschr Med. 2013. PMID: 24260920 Review. German. No abstract available.
-
Evolution of guidelines for pediatric rhinosinusitis.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Sep;77(9):1383-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.06.014. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23845536 Review.
-
Rhinosinusitis: a retrospective analysis of clinical pattern and outcome in north western Nigeria.Ann Afr Med. 2010 Jan-Mar;9(1):20-6. doi: 10.4103/1596-3519.62620. Ann Afr Med. 2010. PMID: 20418645
References
-
- Agence française de sécurité sanitaire des produits de santé . 2005. Antibiothérapie par voie générale en pratique courante dans les infections respiratoires hautes de l’adulte et l’enfant. Recommandations Afssaps. - PubMed
-
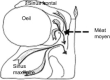
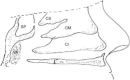
- Wolf G., Anderhuber W., Kuhn F. Development of the paranasal sinuses in children: implications for paranasal sinus surgery. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. 1993;102:705–711. - PubMed
-
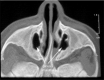
- Spaeth J., Krügelstein U., Schöndorff G. The paranasal sinuses in CT-imaging: development from birth to age 25. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1997;39:25–40. - PubMed
-
- Thorp M.A., Roche P., Nilssen E.L.K., Mortimore S. Complicated acute sinusitis and the computed tomography anatomy of the ostiomeatal unit in childhood. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1999;49:189–195. - PubMed
-
- Weiglein A., Anderuber W., Wolf G. Radiological anatomy of the paranasal sinuses in the child. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 1992;14:335–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

