Techniques used in studies of epigenome dysregulation due to aberrant DNA methylation: an emphasis on fetal-based adult diseases
- PMID: 17317097
- PMCID: PMC2055548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2007.01.004
Techniques used in studies of epigenome dysregulation due to aberrant DNA methylation: an emphasis on fetal-based adult diseases
Abstract
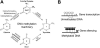
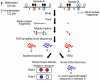
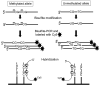
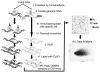
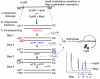
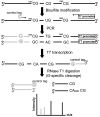
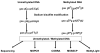
Epigenetic changes are heritable modifications that do not involve alterations in the primary DNA sequence. They regulate crucial cellular functions such as genome stability, X-chromosome inactivation, and gene imprinting. Epidemiological and experimental observations now suggest that such changes may also explain the fetal basis of adult diseases such as cancer, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, neurological diseases, and behavioral modifications. The main molecular events known to initiate and sustain epigenetic modifications are histone modification and DNA methylation. This review specifically focuses on existing and emerging technologies used in studying DNA methylation, which occurs primarily at CpG dinucleotides in the genome. These include standard exploratory tools used for global profiling of DNA methylation and targeted gene investigation: methylation sensitive restriction fingerprinting (MSRF), restriction landmark genomic scanning (RLGS), methylation CpG island amplification-representational difference analysis (MCA-RDA), differential methylation hybridization (DMH), and cDNA microarrays combined with treatment with demethylating agents and inhibitors of histone deacetylase. The basic operating principals, resource requirements, applications, and benefits and limitations of each methodology are discussed. Validation methodologies and functional assays needed to establish the role of a CpG-rich sequence in regulating the expression of a target or candidate gene are outlined. These include in silico database searches, methylation status studies (bisulfite genomic sequencing, COBRA, MS-PCR, MS-SSCP), gene expression studies, and promoter activity analyses. Our intention is to give readers a starting point for choosing methodologies and to suggest a workflow to follow during their investigations. We believe studies of epigenetic changes such as DNA methylation hold great promise in understanding the early origins of adult diseases and in advancing their diagnosis, prevention, and treatment.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Analyzing the cancer methylome through targeted bisulfite sequencing.Cancer Lett. 2013 Nov 1;340(2):171-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.10.040. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23200671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demethylation by 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine in colorectal cancer cells targets genomic DNA whilst promoter CpG island methylation persists.BMC Cancer. 2010 Jul 12;10:366. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-366. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20618997 Free PMC article.
-
[Modern methodical approaches to determining the DNA methylation status and their use in oncology].Ukr Biokhim Zh (1999). 2008 Jul-Aug;80(4):5-15. Ukr Biokhim Zh (1999). 2008. PMID: 19140445 Review. Ukrainian.
-
Alterations in the sperm histone-retained epigenome are associated with unexplained male factor infertility and poor blastocyst development in donor oocyte IVF cycles.Hum Reprod. 2017 Dec 1;32(12):2443-2455. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dex317. Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 29087470
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
Cited by
-
Considerations for normalization of DNA methylation data by Illumina 450K BeadChip assay in population studies.Epigenetics. 2013 Nov;8(11):1141-52. doi: 10.4161/epi.26037. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Epigenetics. 2013. PMID: 23959097 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation within the I.4 promoter region correlates with CYPl19A1 gene expression in human ex vivo mature omental and subcutaneous adipocytes.BMC Med Genet. 2013 Aug 30;14:87. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-14-87. BMC Med Genet. 2013. PMID: 24128150 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of genomic DNA methylation with denaturing high performance liquid chromatography.Hum Cell. 2010 May;23(2):41-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-0774.2010.00084.x. Hum Cell. 2010. PMID: 20712707
-
Healthy lifestyles and wellbeing reduce neuroinflammation and prevent neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders.Front Neurosci. 2023 Feb 15;17:1092537. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1092537. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36875655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphoma and lung cancer in offspring born to pregnant mice dosed with dibenzo[a,l]pyrene: the importance of in utero vs. lactational exposure.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008 Dec 15;233(3):454-8. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.09.009. Epub 2008 Sep 24. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18848954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Y, Freedman BI. Genetics of progressive renal failure in diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2005:S94–S97. - PubMed
-
- Kroll TG. Molecular events in follicular thyroid tumors. Cancer Treat Res. 2004;122:85–105. - PubMed
-
- Moore MA. Converging pathways in leukemogenesis and stem cell self-renewal. Exp Hematol. 2005;33:719–37. - PubMed
-
- Scher HI, Sawyers CL. Biology of progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: directed therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8253–61. - PubMed
-
- Tusie Luna MT. Genes and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Med Res. 2005;36:210–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

