Kinetically competent intermediates in the translocation step of protein synthesis
- PMID: 17317625
- PMCID: PMC1995019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.014
Kinetically competent intermediates in the translocation step of protein synthesis
Abstract
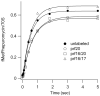
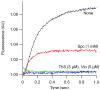
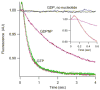
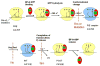
Translocation requires large-scale movements of ribosome-bound tRNAs. Using tRNAs that are proflavin labeled and single-turnover rapid kinetics assays, we identify one or possibly two kinetically competent intermediates in translocation. EF-G.GTP binding to the pretranslocation (PRE) complex and GTP hydrolysis are rapidly followed by formation of the securely identified intermediate complex (INT), which is more slowly converted to the posttranslocation (POST) complex. Peptidyl tRNA within the INT complex occupies a hybrid site, which has a puromycin reactivity intermediate between those of the PRE and POST complexes. Thiostrepton and viomycin inhibit INT formation, whereas spectinomycin selectively inhibits INT disappearance. The effects of other translocation modulators suggest that EF-G-dependent GTP hydrolysis is more important for INT complex formation than for INT complex conversion to POST complex and that subtle changes in tRNA structure influence coupling of tRNA movement to EF-G.GTP-induced conformational changes.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Conformational changes of the small ribosomal subunit during elongation factor G-dependent tRNA-mRNA translocation.J Mol Biol. 2004 Nov 5;343(5):1183-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.08.097. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15491605
-
Role of hybrid tRNA-binding states in ribosomal translocation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jul 8;105(27):9192-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710146105. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18591673 Free PMC article.
-
Translocation dynamics of tRNA-mRNA in the ribosome.Biophys Chem. 2013 Oct-Nov;180-181:22-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Biophys Chem. 2013. PMID: 23811427
-
Synchronous tRNA movements during translocation on the ribosome are orchestrated by elongation factor G and GTP hydrolysis.Bioessays. 2014 Oct;36(10):908-18. doi: 10.1002/bies.201400076. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Bioessays. 2014. PMID: 25118068 Review.
-
[Mechanism of tRNA translocation on the ribosome].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2001 Jul-Aug;35(4):655-65. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2001. PMID: 11524952 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Structural mechanism of GTPase-powered ribosome-tRNA movement.Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 11;12(1):5933. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26133-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34635670 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring translation with modified mRNAs strategically labeled with isomorphic fluorescent guanosine mimetics.ACS Chem Biol. 2013 Sep 20;8(9):2017-23. doi: 10.1021/cb400256h. Epub 2013 Jul 18. ACS Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23865809 Free PMC article.
-
Model of the pathway of -1 frameshifting: Long pausing.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2016 Jan 29;5:408-424. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2016.01.017. eCollection 2016 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2016. PMID: 28955849 Free PMC article.
-
Ataluren and aminoglycosides stimulate read-through of nonsense codons by orthogonal mechanisms.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 12;118(2):e2020599118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2020599118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33414181 Free PMC article.
-
A new view of protein synthesis: mapping the free energy landscape of the ribosome using single-molecule FRET.Biopolymers. 2008 Jul;89(7):565-77. doi: 10.1002/bip.20961. Biopolymers. 2008. PMID: 18286627 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agrawal RK, Linde J, Sengupta J, Nierhaus KH, Frank J. Localization of L11 protein on the ribosome and elucidation of its involvement in EF-G-dependent translocation. J Mol Biol. 2001;311:777–787. - PubMed
-
- Boelens R, Gualerzi CO. Structure and function of bacterial initiation factors. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2002;3:107–119. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

