A versatile ligation-independent cloning method suitable for high-throughput expression screening applications
- PMID: 17317681
- PMCID: PMC1874605
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm047
A versatile ligation-independent cloning method suitable for high-throughput expression screening applications
Abstract
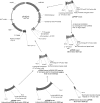
This article describes the construction of a set of versatile expression vectors based on the In-Fusion cloning enzyme and their use for high-throughput cloning and expression screening. Modifications to commonly used vectors rendering them compatible with In-Fusion has produced a ligation-independent cloning system that is (1) insert sequence independent (2) capable of cloning large PCR fragments (3) efficient over a wide (20-fold) insert concentration range and (4) applicable to expression in multiple hosts. The system enables the precise engineering of (His(6)-) tagged constructs with no undesirable vector or restriction-site-derived amino acids added to the expressed protein. The use of a multiple host-enabled vector allows rapid screening in both E. coli and eukaryotic hosts (HEK293T cells and insect cell hosts, e.g. Sf9 cells). These high-throughput screening activities have prompted the development and validation of automated protocols for transfection of mammalian cells and Ni-NTA protein purification.
Figures

References
-
- Klock HE, White A, Koesema E, Lesley SA. Methods and results for semi-automated cloning using integrated robotics. J. Struct. Funct. Genomics. 2005;6:89–94. - PubMed
-
- Alzari P, Berglund H, Berrow NS, Blagova E, Busso D, Cambillau C, Campanacci V, Christodoulo E, Eiler S, et al. Implementation of semi-automated cloning and prokaryotic expression screening: the impact of SPINE. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2005;D62:1103–1113. - PubMed
-
- Haun RS, Serventi IM, Moss J. Rapid, reliable ligation-independent cloning of PCR products using modified plasmid vectors. Biotechniques. 1992;13:515–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

