Interactions of Kid-Kis toxin-antitoxin complexes with the parD operator-promoter region of plasmid R1 are piloted by the Kis antitoxin and tuned by the stoichiometry of Kid-Kis oligomers
- PMID: 17317682
- PMCID: PMC1865072
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm073
Interactions of Kid-Kis toxin-antitoxin complexes with the parD operator-promoter region of plasmid R1 are piloted by the Kis antitoxin and tuned by the stoichiometry of Kid-Kis oligomers
Abstract
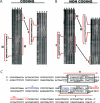
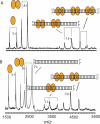
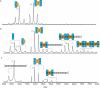
The parD operon of Escherichia coli plasmid R1 encodes a toxin-antitoxin system, which is involved in plasmid stabilization. The toxin Kid inhibits cell growth by RNA degradation and its action is neutralized by the formation of a tight complex with the antitoxin Kis. A fascinating but poorly understood aspect of the kid-kis system is its autoregulation at the transcriptional level. Using macromolecular (tandem) mass spectrometry and DNA binding assays, we here demonstrate that Kis pilots the interaction of the Kid-Kis complex in the parD regulatory region and that two discrete Kis-binding regions are present on parD. The data clearly show that only when the Kis concentration equals or exceeds the Kid concentration a strong cooperative effect exists between strong DNA binding and Kid2-Kis2-Kid2-Kis2 complex formation. We propose a model in which transcriptional repression of the parD operon is tuned by the relative molar ratio of the antitoxin and toxin proteins in solution. When the concentration of the toxin exceeds that of the antitoxin tight Kid2-Kis2-Kid2 complexes are formed, which only neutralize the lethal activity of Kid. Upon increasing the Kis concentration, (Kid2-Kis2)n complexes repress the kid-kis operon.
Figures
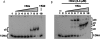


Similar articles
-
Interactions between the toxin Kid of the bacterial parD system and the antitoxins Kis and MazE.Proteins. 2007 Apr 1;67(1):219-31. doi: 10.1002/prot.21254. Proteins. 2007. PMID: 17206710
-
Cleavage of the antitoxin of the parD toxin-antitoxin system is determined by the ClpAP protease and is modulated by the relative ratio of the toxin and the antitoxin.Plasmid. 2013 Jul;70(1):78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2013.01.010. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Plasmid. 2013. PMID: 23419648
-
Genetic identification of two functional regions in the antitoxin of the parD killer system of plasmid R1.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002 Jan 2;206(1):115-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb10995.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002. PMID: 11786266
-
Structure and function of bacterial kid-kis and related toxin-antitoxin systems.Protein Pept Lett. 2007;14(2):113-24. doi: 10.2174/092986607779816096. Protein Pept Lett. 2007. PMID: 17305597 Review.
-
parD toxin-antitoxin system of plasmid R1--basic contributions, biotechnological applications and relationships with closely-related toxin-antitoxin systems.FEBS J. 2010 Aug;277(15):3097-117. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07722.x. Epub 2010 Jun 21. FEBS J. 2010. PMID: 20569269 Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding the TAome and computational insights into parDE toxin-antitoxin systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Jul 27;206(8):360. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04085-2. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39066828
-
An intrinsically disordered entropic switch determines allostery in Phd-Doc regulation.Nat Chem Biol. 2016 Jul;12(7):490-6. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2078. Epub 2016 May 2. Nat Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27159580
-
Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacterial growth arrest and persistence.Nat Chem Biol. 2016 Apr;12(4):208-14. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2044. Nat Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 26991085 Review.
-
RelB and RelE of Escherichia coli form a tight complex that represses transcription via the ribbon-helix-helix motif in RelB.J Mol Biol. 2009 Nov 27;394(2):183-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.09.006. Epub 2009 Sep 8. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19747491 Free PMC article.
-
Functional insights into the Streptococcus pneumoniae HicBA toxin-antitoxin system based on a structural study.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 6;46(12):6371-6386. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky469. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29878152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayes F. Toxins-antitoxins: plasmid maintenance, programmed cell death, and cell cycle arrest. Science. 2003;301:1496–1499. - PubMed
-
- Gerdes K, Christensen SK, Lobner-Olesen A. Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin stress response loci. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005;3:371–382. - PubMed
-
- Bernard P, Couturier M. Cell killing by the F-plasmid Ccdb protein involves poisoning of DNA-topoisomerase-Ii complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 1992;226:735–745. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, Pogliano J, Helinski DR, Konieczny I. ParE toxin encoded by the broad-host-range plasmid RK2 is an inhibitor of Escherichia coli gyrase. Mol. Microbiol. 2002;44:971–979. - PubMed

