In the developing rat hippocampus a tonic GABAA-mediated conductance selectively enhances the glutamatergic drive of principal cells
- PMID: 17317750
- PMCID: PMC2075167
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.125609
In the developing rat hippocampus a tonic GABAA-mediated conductance selectively enhances the glutamatergic drive of principal cells
Abstract
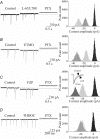
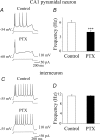
In the adult hippocampus, two different forms of GABA(A) receptor-mediated inhibition have been identified: phasic and tonic. The first is due to the activation of GABA(A) receptors facing the presynaptic releasing sites, whereas the second is due to the activation of receptors localized away from the synapses. Because of their high affinity and low desensitization rate, extrasynaptic receptors are persistently able to sense low concentrations of GABA. Here we show that, early in postnatal life, between postnatal day (P) 2 and P6, CA1 and CA3 pyramidal cells but not stratum radiatum interneurons, express a tonic GABA(A)-mediated conductance. Block of the neuronal GABA transporter GAT-1 slightly enhanced the persistent GABA conductance in principal cells but not in GABAergic interneurons. However, in adulthood, a tonic GABA(A)-mediated conductance could be revealed in stratum radiatum interneurons, indicating that the ability of these cells to sense ambient GABA levels is developmentally regulated. Pharmacological analysis of the tonic conductance in principal cells demonstrated the involvement of beta2/beta 3, alpha 5 and gamma 2 GABA(A) receptor subunits. Removal of the tonic depolarizing action of GABA with picrotoxin, reduced the excitability and the glutamatergic drive of principal cells but did not modify the excitability of stratum radiatum interneurons. The increased cell excitability and synaptic activity following the activation of extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors by ambient GABA would facilitate the induction of giant depolarizing potentials.
Figures




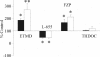


Similar articles
-
Subtype-specific GABA transporter antagonists synergistically modulate phasic and tonic GABAA conductances in rat neocortex.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Sep;94(3):2073-85. doi: 10.1152/jn.00520.2005. Epub 2005 Jun 29. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15987761
-
GABA uptake regulates cortical excitability via cell type-specific tonic inhibition.Nat Neurosci. 2003 May;6(5):484-90. doi: 10.1038/nn1043. Nat Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12679782
-
GABAergic signaling at mossy fiber synapses in neonatal rat hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2006 Jan 11;26(2):597-608. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4493-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16407558 Free PMC article.
-
Seizures beget seizures: the quest for GABA as a key player.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):135-44. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.140. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725516 Review.
-
Pathophysiological power of improper tonic GABA(A) conductances in mature and immature models.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 Oct 24;7:170. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00170. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 24167475 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neonatal phenobarbital exposure disrupts GABAergic synaptic maturation in rat CA1 neurons.Epilepsia. 2018 Feb;59(2):333-344. doi: 10.1111/epi.13990. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Epilepsia. 2018. PMID: 29315524 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic localization of α5 GABA (A) receptors via gephyrin interaction regulates dendritic outgrowth and spine maturation.Dev Neurobiol. 2015 Nov;75(11):1241-51. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22280. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Dev Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25663431 Free PMC article.
-
Transition to seizures in the isolated immature mouse hippocampus: a switch from dominant phasic inhibition to dominant phasic excitation.J Physiol. 2008 Jan 15;586(2):477-94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.143065. Epub 2007 Nov 8. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 17991696 Free PMC article.
-
GABA neurons and the mechanisms of network oscillations: implications for understanding cortical dysfunction in schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 2008 Sep;34(5):944-61. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbn070. Epub 2008 Jun 26. Schizophr Bull. 2008. PMID: 18586694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABA and glycine in the developing brain.J Physiol Sci. 2016 Sep;66(5):375-9. doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0442-7. Epub 2016 Mar 7. J Physiol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26951057 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bai D, Zhu G, Pennefather P, Jackson MF, MacDonald JF, Orser BA. Distinct functional and pharmacological properties of tonic and quantal inhibitory postsynaptic currents mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors in hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 2001;59:814–824. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Excitatory actions of GABA during development: the nature of the nurture. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:728–739. - PubMed
-
- Bolea S, Avignone E, Berretta N, Sanchez-Andres JV, Cherubini E. Glutamate controls the induction of GABA-mediated giant depolarizing potentials through AMPA receptors in neonatal rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol. 1999;81:2095–2102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

