The effect of a single nucleotide polymorphism on human alpha 2-antiplasmin activity
- PMID: 17317851
- PMCID: PMC1890835
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-065185
The effect of a single nucleotide polymorphism on human alpha 2-antiplasmin activity
Abstract
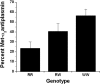
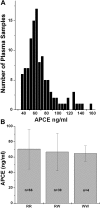
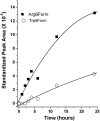
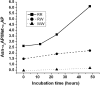
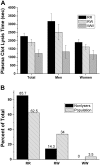
The primary inhibitor of plasmin, alpha(2)-antiplasmin (alpha(2)AP), is secreted by the liver into plasma with Met as the amino-terminus. During circulation, Met-alpha(2)AP is cleaved by antiplasmin-cleaving enzyme (APCE), yielding Asn-alpha(2)AP, which is crosslinked into fibrin approximately 13 times faster than Met-alpha(2)AP. The Met-alpha(2)AP gene codes for either Arg or Trp as the sixth amino acid, with both polymorphic forms found in human plasma samples. We determined the Arg6Trp genotype frequency in a healthy population and its effects on Met-alpha(2)AP cleavage and fibrinolysis. Genotype frequencies were RR 62.5%, RW 34.0%, and WW 3.5%. The polymorphism related to the percentage of Met-alpha(2)AP in plasma was WW (56.4%), RW (40.6%), and RR (23.6%). WW plasma tended to have shorter lysis times than RR and RW plasmas. APCE cleaved purified Met-alpha(2)AP(Arg6) approximately 8-fold faster than Met-alpha(2)AP(Trp6), which is reflected in Asn-alpha(2)AP/Met-alpha(2)AP ratios with time in RR, RW, and WW plasmas. Removal of APCE from plasma abrogated cleavage of Met-alpha(2)AP. We conclude that the Arg6Trp polymorphism is functionally significant, as it clearly affects conversion of Met-alpha(2)AP to Asn-alpha(2)AP, and thereby, the rate of alpha(2)AP incorporation into fibrin. Therefore, the Arg6Trp polymorphism may play a significant role in governing the long-term deposition/removal of intravascular fibrin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Why alpha-antiplasmin must be converted to a derivative form for optimal function.J Thromb Haemost. 2007 Oct;5(10):2095-104. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02707.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2007. PMID: 17883704
-
Enhancement of fibrinolysis by inhibiting enzymatic cleavage of precursor α2-antiplasmin.J Thromb Haemost. 2011 May;9(5):987-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04195.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2011. PMID: 21251197 Free PMC article.
-
A novel plasma proteinase potentiates alpha2-antiplasmin inhibition of fibrin digestion.Blood. 2004 May 15;103(10):3783-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-12-4240. Epub 2004 Jan 29. Blood. 2004. PMID: 14751930
-
Alpha2-antiplasmin: potential therapeutic roles in fibrin survival and removal.Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2004 Oct;2(4):303-10. doi: 10.2174/1568016043356228. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2004. PMID: 15320781 Review.
-
Gene targeting in hemostasis. Alpha2-antiplasmin.Front Biosci. 2001 Feb 1;6:D239-47. doi: 10.2741/lijnen. Front Biosci. 2001. PMID: 11171550 Review.
Cited by
-
SERPINs-From Trap to Treatment.Front Med (Lausanne). 2019 Feb 12;6:25. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00025. eCollection 2019. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30809526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence that alpha2-antiplasmin becomes covalently ligated to plasma fibrinogen in the circulation: a new role for plasma factor XIII in fibrinolysis regulation.J Thromb Haemost. 2008 Sep;6(9):1565-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03056.x. Epub 2008 Jun 16. J Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 18564219 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporation of α2-Plasmin Inhibitor into Fibrin Clots and Its Association with the Clinical Outcome of Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 25;11(3):347. doi: 10.3390/biom11030347. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33669007 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Physical Mechanisms of Fibrinolysis and Thrombolysis from Mathematical Modeling and Experiments.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 7;7(1):6914. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06383-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28785035 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the N-terminus of alpha-2-antiplasmin.PLoS One. 2018 May 3;13(5):e0196911. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196911. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29723259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collen D. The plasminogen (fibrinolytic) system. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82:259–270. - PubMed
-
- Wiman B, Collen D. On the kinetics of the reaction between human antiplasmin and plasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1978;84:573–578. - PubMed
-
- Collen D. Identification and some properties of a new fast-reacting plasmin inhibitor in human plasma. Eur J Biochem. 1976;69:209–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

