Abnormal thyroid hormone metabolism in mice lacking the monocarboxylate transporter 8
- PMID: 17318265
- PMCID: PMC1797602
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI28253
Abnormal thyroid hormone metabolism in mice lacking the monocarboxylate transporter 8
Abstract
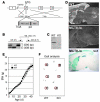
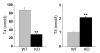
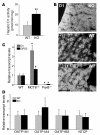
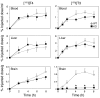
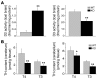
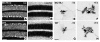
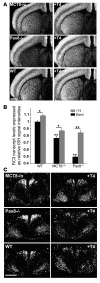
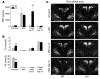
In humans, inactivating mutations in the gene of the thyroid hormone transporter monocarboxylate transporter 8 (MCT8; SLC16A2) lead to severe forms of psychomotor retardation combined with imbalanced thyroid hormone serum levels. The MCT8-null mice described here, however, developed without overt deficits but also exhibited distorted 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) serum levels, resulting in increased hepatic activity of type 1 deiodinase (D1). In the mutants' brains, entry of T4 was not affected, but uptake of T3 was diminished. Moreover, the T4 and T3 content in the brain of MCT8-null mice was decreased, the activity of D2 was increased, and D3 activity was decreased, indicating the hypothyroid state of this tissue. In the CNS, analysis of T3 target genes revealed that in the mutants, the neuronal T3 uptake was impaired in an area-specific manner, with strongly elevated thyrotropin-releasing hormone transcript levels in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and slightly decreased RC3 mRNA expression in striatal neurons; however, cerebellar Purkinje cells appeared unaffected, since they did not exhibit dendritic outgrowth defects and responded normally to T3 treatment in vitro. In conclusion, the circulating thyroid hormone levels of MCT8-null mice closely resemble those of humans with MCT8 mutations, yet in the mice, CNS development is only partially affected.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional neuroanatomy of thyroid hormone feedback in the human hypothalamus and pituitary gland.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2006 Jun 7;251(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2006.03.042. Epub 2006 May 16. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16707210 Review.
-
Impact of monocarboxylate transporter-8 deficiency on the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis in mice.Endocrinology. 2010 Oct;151(10):5053-62. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0593. Epub 2010 Aug 11. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20702572
-
Tissue-specific thyroid hormone deprivation and excess in monocarboxylate transporter (mct) 8-deficient mice.Endocrinology. 2006 Sep;147(9):4036-43. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-0390. Epub 2006 May 18. Endocrinology. 2006. PMID: 16709608
-
Consequences of monocarboxylate transporter 8 deficiency for renal transport and metabolism of thyroid hormones in mice.Endocrinology. 2010 Feb;151(2):802-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1053. Epub 2009 Dec 8. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 19996182
-
Mechanisms of disease: psychomotor retardation and high T3 levels caused by mutations in monocarboxylate transporter 8.Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Sep;2(9):512-23. doi: 10.1038/ncpendmet0262. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16957765 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-Specific Transport and Thyroid Hormone Receptor Isoform Selectivity Account for Hepatocyte-Targeted Thyromimetic Action of MGL-3196.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 8;23(22):13714. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213714. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430194 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacodynamics Research on Danggui-Shaoyao-San through Body Fluid Indexes of Spleen Deficiency-water Dampness Rats using Bio-impedance Technology.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(12):1602-1616. doi: 10.2174/0113892010243018231025065109. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37921128
-
Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism.Physiol Rev. 2014 Apr;94(2):355-82. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2013. Physiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24692351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Desensitization and Incomplete Recovery of Hepatic Target Genes After Chronic Thyroid Hormone Treatment and Withdrawal in Male Adult Mice.Endocrinology. 2016 Apr;157(4):1660-72. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1848. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 26866609 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin-induced inflammation down-regulates L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) expression at the blood-brain barrier of male rats and mice.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2015 Sep 4;12:21. doi: 10.1186/s12987-015-0016-8. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2015. PMID: 26337286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Porterfield S.P., Hendrich C.E. The role of thyroid hormones in prenatal and neonatal neurological development — current perspectives. Endocr. Rev. 1993;14:94–106. - PubMed
-
- Oppenheimer J.H., Schwartz H.L. Molecular basis of thyroid hormone-dependent brain development. Endocr. Rev. 1997;18:462–475. - PubMed
-
- de Escobar G.M., Obregon M.J., del Rey F.E. Maternal thyroid hormones early in pregnancy and fetal brain development. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2004;18:225–248. - PubMed
-
- Jones S.A., Thoemke K.R., Anderson G.W. The role of thyroid hormone in fetal and neonatal brain development. Current Opinion in Endocrinology and Diabetes. 2005;12:10–16.
-
- Bernal J. Thyroid hormones and brain development. Vitam. Horm. 2005;71:95–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

