GridIMAGE: a novel use of grid computing to support interactive human and computer-assisted detection decision support
- PMID: 17318701
- PMCID: PMC1896264
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-007-9020-0
GridIMAGE: a novel use of grid computing to support interactive human and computer-assisted detection decision support
Abstract
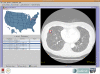
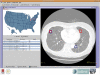
This paper describes a Grid-aware image reviewing system (GridIMAGE) that allows practitioners to (a) select images from multiple geographically distributed digital imaging and communication in medicine (DICOM) servers, (b) send those images to a specified group of human readers and computer-assisted detection (CAD) algorithms, and (c) obtain and compare interpretations from human readers and CAD algorithms. The currently implemented system was developed using the National Cancer Institute caGrid infrastructure and is designed to support the identification of lung nodules on thoracic computed tomography. However, the infrastructure is general and can support any type of distributed review. caGrid data and analytical services are used to link DICOM image databases and CAD systems and to interact with human readers. Moreover, the service-oriented and distributed structure of the GridIMAGE framework enables a flexible system, which can be deployed in an institution (linking multiple DICOM servers and CAD algorithms) and in a Grid environment (linking the resources of collaborating research groups). GridIMAGE provides a framework that allows practitioners to obtain interpretations from one or more human readers or CAD algorithms. It also provides a mechanism to allow cooperative imaging groups to systematically perform image interpretation tasks associated with research protocols.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Informatics in radiology: GridCAD: grid-based computer-aided detection system.Radiographics. 2007 May-Jun;27(3):889-97. doi: 10.1148/rg.273065153. Radiographics. 2007. PMID: 17495299 Review.
-
PET/CT image navigation and communication.J Nucl Med. 2004 Jan;45 Suppl 1:46S-55S. J Nucl Med. 2004. PMID: 14736835 Review.
-
Integration of the digital imaging and communications in medicine standard into an oral and maxillofacial image management and communication system.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001 Feb;91(2):235-8. doi: 10.1067/moe.2001.111941. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001. PMID: 11174603
-
DicomWorks: software for reviewing DICOM studies and promoting low-cost teleradiology.J Digit Imaging. 2007 Jun;20(2):122-30. doi: 10.1007/s10278-007-9018-7. J Digit Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17333414 Free PMC article.
-
An automated PACS image acquisition and recovery scheme for image integrity based on the DICOM standard.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 1997 Jul-Aug;21(4):209-18. doi: 10.1016/s0895-6111(97)00011-6. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 1997. PMID: 9402233
Cited by
-
e-Science, caGrid, and Translational Biomedical Research.Computer (Long Beach Calif). 2008 Nov;41(11):58-66. doi: 10.1109/MC.2008.459. Computer (Long Beach Calif). 2008. PMID: 21311723 Free PMC article.
-
A knowledge-anchored integrative image search and retrieval system.J Digit Imaging. 2009 Apr;22(2):166-82. doi: 10.1007/s10278-007-9086-8. Epub 2007 Nov 27. J Digit Imaging. 2009. PMID: 18040742 Free PMC article.
-
Sharing data and analytical resources securely in a biomedical research Grid environment.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2008 May-Jun;15(3):363-73. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M2662. Epub 2008 Feb 28. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2008. PMID: 18308979 Free PMC article.
-
The Empirical Foundations of Teleradiology and Related Applications: A Review of the Evidence.Telemed J E Health. 2016 Nov;22(11):868-898. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2016.0149. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Telemed J E Health. 2016. PMID: 27585301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
caGrid 1.0: a Grid enterprise architecture for cancer research.AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2007 Oct 11;2007:573-7. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2007. PMID: 18693901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- OSU Department of Biomedical Informatics: Biomedical Informatics Department Web Page. http://www.bmi.osu.edu. Accessed November 23, 2006
-
- Hastings SL, Langella S, Oster S, Saltz JH: Distributed data management and integration framework: The Mobius Project. In: Proceedings of the Global Grid Forum 11 (GGF11) Semantic Grid Applications Workshop. Global Grid Forum, Lemont, 2004, p 20
-
- Berman F, Hey AJ, Fox G. Grid Computing: Making the Global Infrastructure a Reality. New York: Wiley; 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

