Serial changes in plasma levels of cytokines in patients with coronary artery disease
- PMID: 17319110
- PMCID: PMC1993951
Serial changes in plasma levels of cytokines in patients with coronary artery disease
Abstract
Objectives: Inflammation is known to be a major determinant of the progression of coronary artery disease (CAD). In the present study we have evaluated the plasma levels of cytokines-tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF), interleukin- 1 alpha (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interferon-gamma (IFN), and interleukin-10 (IL-10)- to examine the association between these cytokines and C-reactive protein (CRP) in patients with CAD.
Methods: Patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS; n = 20) were compared with patients with stable angina (SA; n= 20) and with control volunteers (C; n= 20). Blood samples were collected at the time of admission from all patients and 15 and 30 days thereafter.
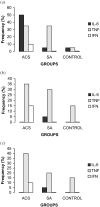
Results: CRP levels (20.8+/-8.8 mg/L) (mean+/-SEM) were higher at baseline in ACS than SA patients (4.1+/-0.8mg/L) or the control subjects (5.1+/-1.8mg/L) (p<0.05). At admission, IL-6 was detected in 50% of the ACS patients and 5% of the SA patients or control subjects, while TNF was detected in 35% of the ACS and SA patients but only in 5% of control subjects. Subsequently, IL-6 levels declined and were no longer detectable, while TNF levels increased among ACS patients at all time periods tested when compared with other patients. The presence of IL-1 and IL-10 were not detectable in the blood samples examined, and IFN could only be detected in the ACS group. A significant correlation was observed between IL-6 and CRP levels (r=0.4; p<0.01) in all groups. There were no correlations among any of the other cytokines and CRP levels.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates raised levels of TNF, IL-6, IFN, and CRP in patients with ACS and a positive correlation between IL-6 and CRP but not with the other cytokines.
Figures
References
-
- Amento EP, Ehsani N, Palmer H, et al. Cytokines positively and negatively regulate interstitial collagen gene expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991;11:1223–30. - PubMed
-
- Biasucci LM, Vitelli A, Liuzzo G, et al. Elevated levels of interleukin-6 in unstable angina. Circulation. 1996;94:874–7. - PubMed
-
- Braunwald E. Unstable angina: a classification. Circulation. 1989;80:410–14. - PubMed
-
- Caligiuri G, Liuzzo G, Biasucci LM, et al. Immune system activation follows inflammation in unstable angina: pathogenetic implications. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;32:1295–304. - PubMed
-
- Danesh J, Wheeler JG, Hirschfield GM, et al. C-reactive protein and other circulating markers of inflammation in the prediction of coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1387–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
