Antagonism between Notch and bone morphogenetic protein receptor signaling regulates neurogenesis in the cerebellar rhombic lip
- PMID: 17319963
- PMCID: PMC1820780
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-8104-2-5
Antagonism between Notch and bone morphogenetic protein receptor signaling regulates neurogenesis in the cerebellar rhombic lip
Abstract
Background: During the embryonic development of the cerebellum, neurons are produced from progenitor cells located along a ventricular zone within dorsal rhombomere 1 that extends caudally to the roof plate of the fourth ventricle. The apposition of the caudal neuroepithelium and roof plate results in a unique inductive region termed the cerebellar rhombic lip, which gives rise to granule cell precursors and other glutamatergic neuronal lineages. Recently, we and others have shown that, at early embryonic stages prior to the emergence of granule cell precursors (E12), waves of neurogenesis in the cerebellar rhombic lip produce specific hindbrain nuclei followed by deep cerebellar neurons. How the induction of rhombic lip-derived neurons from cerebellar progenitors is regulated during this phase of cerebellar development to produce these temporally discrete neuronal populations while maintaining a progenitor pool for subsequent neurogenesis is not known.
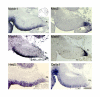
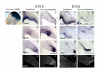
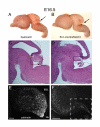
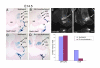
Results: Employing both gain- and loss-of-function methods, we find that Notch1 signaling in the cerebellar primordium regulates the responsiveness of progenitor cells to bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) secreted from the roof plate that stimulate the production of rhombic lip-derived neurons. In the absence of Notch1, cerebellar progenitors are depleted during the early production of hindbrain neurons, resulting in a severe decrease in the deep cerebellar nuclei that are normally born subsequently. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that Notch1 activity prevents the induction of Math1 by antagonizing the BMP receptor-signaling pathway at the level of Msx2 expression.
Conclusion: Our results provide a mechanism by which a balance between neural induction and maintenance of neural progenitors is achieved in the rhombic lip throughout embryonic development.
Figures

References
-
- Akazawa C, Ishibashi M, Shimizu C, Nakanishi S, Kageyama R. A mammalian helix-loop-helix factor structurally related to the product of Drosophila proneural gene atonal is a positive transcriptional regulator expressed in the developing nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:8730–8738. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.1342. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

