Molecular mechanisms mediating the G protein-coupled receptor regulation of cell cycle progression
- PMID: 17319972
- PMCID: PMC1808056
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-2187-2-2
Molecular mechanisms mediating the G protein-coupled receptor regulation of cell cycle progression
Abstract
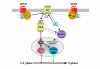
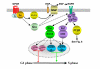
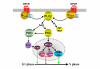
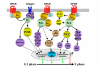
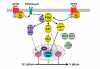
G protein-coupled receptors are key regulators of cellular communication, mediating the efficient coordination of a cell's responses to extracellular stimuli. When stimulated these receptors modulate the activity of a wide range of intracellular signalling pathways that facilitate the ordered development, growth and reproduction of the organism. There is now a growing body of evidence examining the mechanisms by which G protein-coupled receptors are able to regulate the expression, activity, localization and stability of cell cycle regulatory proteins that either promote or inhibit the initiation of DNA synthesis. In this review, we will detail the intracellular pathways that mediate the G protein-coupled receptor regulation of cellular proliferation, specifically the progression from the G1 phase to the S phase of the cell cycle.
Figures

References
-
- Moolenaar WH. G-protein-coupled receptors, phosphoinositide hydrolysis, and cell proliferation. Cell Growth Differen. 1991;2:359–64. - PubMed
-
- Li S, Huang S, Peng SB. Overexpression of G protein-coupled receptors in cancer cells: involvement in tumor progression. Int J Oncol. 2005;27:1329–1339. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

