Human and macaque pupil responses driven by melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells
- PMID: 17320141
- PMCID: PMC1945238
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2006.12.015
Human and macaque pupil responses driven by melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells
Abstract
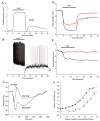
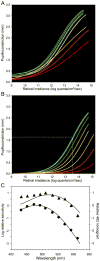
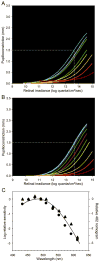
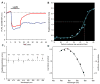
Melanopsin, a novel photopigment, has recently been localized to a population of retinal ganglion cells that display inherent photosensitivity. During continuous light and following light offset, primates are known to exhibit sustained pupilloconstriction responses that resemble closely the photoresponses of intrinsically-photoreceptive ganglion cells. We report that, in the behaving macaque, following pharmacological blockade of conventional photoreceptor signals, significant pupillary responses persist during continuous light and following light offset. These pupil responses display the unique spectral tuning, slow kinetics, and irradiance coding of the sustained, melanopsin-derived ganglion cell photoresponses. We extended our observations to humans by using the sustained pupil response following light offset to document the contribution of these novel ganglion cells to human pupillary responses. Our results indicate that the intrinsic photoresponses of intrinsically-photoreceptive retinal ganglion cells play an important role in the pupillary light reflex and are primarily responsible for the sustained pupilloconstriction that occurs following light offset.
Figures
References
-
- Alpern M, Campbell FW. The behaviour of the pupil during dark-adaptation. J Physiol Lond. 1962;165:5–7p.
-
- Alpern M, Ohba N. The effect of bleaching and backgrounds on pupil size. Vision Res. 1972;12:943–951. - PubMed
-
- Berson DM, Dunn FA, Takao M. Phototransduction by retinal ganglion cells that set the circadian clock. Science. 2002;295:1070–1073. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 EY006837/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014596/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 EY006837/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 EY006837/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY00901/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY06678/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY009380/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY06837/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY14596/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY006678/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY003039/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY009625/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC006904/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- EY09380/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY09625/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY000901/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

