Pneumocystis murina MSG gene family and the structure of the locus associated with its transcription
- PMID: 17320432
- PMCID: PMC2063445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fgb.2007.01.004
Pneumocystis murina MSG gene family and the structure of the locus associated with its transcription
Abstract
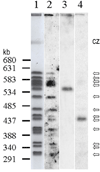
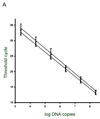
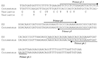
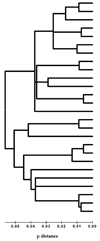
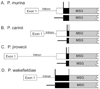
Analysis of the Pneumocystis murina MSG gene family and expression-site locus showed that, as in Pneumocystis carinii, P. murina MSG genes are arranged in head-to-tail tandem arrays located on multiple chromosomes, and that a variety of MSG genes can reside at the unique P. murina expression site. Located between the P. murina expression site and attached MSG gene is a block of 132 basepairs that is also present at the beginning of MSG genes that are not at the expression site. The center of this sequence block resembles the 28 basepair CRJE of P. carinii, but the block of conserved sequence in P. murina is nearly five times longer than in P. carinii, and much shorter than in P. wakefieldiae. These data indicate that the P. murina expression-site locus has a distinct structure.
Figures




References
-
- Armstrong MY, Cushion MT. Animal Models. In: Walzer PD, editor. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. 2nd. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1994. pp. 181–222.
-
- Bishop R, Gurnell J, Laakkonen J, Whitwell K, Peters S. Detection of Pneumocystis DNA in the lungs of several species of wild mammal. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1997;44:57S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

