Histone H3-K56 acetylation is catalyzed by histone chaperone-dependent complexes
- PMID: 17320445
- PMCID: PMC1853276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.02.006
Histone H3-K56 acetylation is catalyzed by histone chaperone-dependent complexes
Abstract
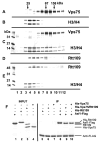
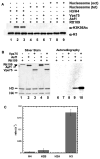
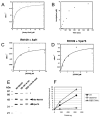
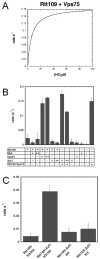
Acetylation of histone H3 on lysine 56 occurs during mitotic and meiotic S phase in fungal species. This acetylation blocks a direct electrostatic interaction between histone H3 and nucleosomal DNA, and the absence of this modification is associated with extreme sensitivity to genotoxic agents. We show here that H3-K56 acetylation is catalyzed when Rtt109, a protein that lacks significant homology to known acetyltransferases, forms an active complex with either of two histone binding proteins, Asf1 or Vps75. Rtt109 binds to both these cofactors, but not to histones alone, forming enzyme complexes with kinetic parameters similar to those of known histone acetyltransferase (HAT) enzymes. Therefore, H3-K56 acetylation is catalyzed by a previously unknown mechanism that requires a complex of two proteins: Rtt109 and a histone chaperone. Additionally, these complexes are functionally distinct, with the Rtt109/Asf1 complex, but not the Rtt109/Vps75 complex, being critical for resistance to genotoxic agents.
Figures
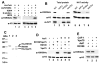


Similar articles
-
Acetylation of lysine 56 of histone H3 catalyzed by RTT109 and regulated by ASF1 is required for replisome integrity.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28587-28596. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702496200. Epub 2007 Aug 9. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17690098
-
Molecular functions of the histone acetyltransferase chaperone complex Rtt109-Vps75.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Sep;15(9):948-56. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1459. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 19172748 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing targeted mass spectrometry to demonstrate Asf1-dependent increases in residue specificity for Rtt109-Vps75 mediated histone acetylation.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0118516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118516. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25781956 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding histone acetyltransferase Rtt109 structure and function: how many chaperones does it take?Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2011 Dec;21(6):728-34. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2011.09.005. Epub 2011 Oct 23. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 22023828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone H3 lysine 56 acetylation: a new twist in the chromosome cycle.Cell Cycle. 2006 Nov;5(22):2602-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.22.3473. Epub 2006 Nov 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 17172838 Review.
Cited by
-
Stoichiometry of Rtt109 complexes with Vps75 and histones H3-H4.Life Sci Alliance. 2020 Sep 10;3(11):e202000771. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202000771. Print 2020 Nov. Life Sci Alliance. 2020. PMID: 32913112 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of chromatin-associated proteins in Sordaria macrospora reveals similar roles for RTT109 and ASF1 in development and DNA damage response.G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Mar 6;14(3):jkae019. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae019. G3 (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 38261383 Free PMC article.
-
Rtt109 prevents hyper-amplification of ribosomal RNA genes through histone modification in budding yeast.PLoS Genet. 2013 Apr;9(4):e1003410. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003410. Epub 2013 Apr 4. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23593017 Free PMC article.
-
The circular logic of mRNA homeostasis.Transcription. 2023 Nov;14(1-2):18-26. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2023.2183684. Epub 2023 Feb 26. Transcription. 2023. PMID: 36843061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of chromatin assembly/disassembly by Rtt109p, a histone H3 Lys56-specific acetyltransferase, in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 1;285(40):30472-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.113225. Epub 2010 Jul 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20668333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adkins MW, Carson JJ, English CM, Ramey CJ, Tyler JK. The histone chaperone anti-silencing function 1 stimulates the acetylation of newly synthesized histone H3 in S-phase. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:1334–1340. - PubMed
-
- Berndsen CE, Denu JM. Assays for mechanistic investigations of protein/histone acetyltransferases. Methods. 2005;36:321–331. - PubMed
-
- Celic I, Masumoto H, Griffith WP, Meluh P, Cotter RJ, Boeke JD, Verreault A. The sirtuins hst3 and hst4p preserve genome integrity by controlling histone h3 lysine 56 deacetylation. Curr Biol. 2006;16:1280–1289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

