The epigenomics of cancer
- PMID: 17320506
- PMCID: PMC3894624
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.029
The epigenomics of cancer
Abstract
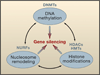
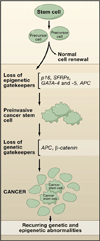
Aberrant gene function and altered patterns of gene expression are key features of cancer. Growing evidence shows that acquired epigenetic abnormalities participate with genetic alterations to cause this dysregulation. Here, we review recent advances in understanding how epigenetic alterations participate in the earliest stages of neoplasia, including stem/precursor cell contributions, and discuss the growing implications of these advances for strategies to control cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Akiyama Y, Watkins N, Suzuki H, Jair KW, van Engeland M, Esteller M, Sakai H, Ren CY, Yuasa Y, Herman JG, Baylin SB. GATA-4 and GATA-5 transcription factor genes and potential downstream antitumor target genes are epigenetically silenced in colorectal and gastric cancer. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003;23:8429–8439. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakker J, Lin X, Nelson WG. Methyl-CpG binding domain protein 2 represses transcription from hypermethylated pi-class glutathione S-transferase gene promoters in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:22573–22580. - PubMed
-
- Baylin SB, Ohm JE. Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer - a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway addiction? Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006;6:107–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

