Intraretinal projection of retinal ganglion cell axons as a model system for studying axon navigation
- PMID: 17320832
- PMCID: PMC2267003
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.116
Intraretinal projection of retinal ganglion cell axons as a model system for studying axon navigation
Abstract
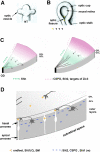
The initial step of retinal ganglion cell (RGC) axon pathfinding involves directed growth of RGC axons toward the center of the retina, the optic disc, a process termed "intraretinal guidance". Due to the accessibility of the system, and with various embryological, molecular and genetic approaches, significant progress has been made in recent years toward understanding the mechanisms involved in the precise guidance of the RGC axons. As axons are extending from RGCs located throughout the retina, a multitude of factors expressed along with the differentiation wave are important for the guidance of the RGC axons. To ensure that the RGC axons are oriented correctly, restricted to the optic fiber layer (OFL) of the retina, and exit the eye properly, different sets of positive and negative factors cooperate in the process. Fasciculation mediated by a number of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) and modulation of axonal response to guidance factors provide additional mechanisms to ensure proper guidance of the RGC axons. The intraretinal axon guidance thus serves as an excellent model system for studying how different signals are regulated, modulated and integrated for guiding a large number of axons in three-dimensional space.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heparan sulfate regulates intraretinal axon pathfinding by retinal ganglion cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Aug 22;52(9):6671-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7559. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21743013 Free PMC article.
-
DSCAM promotes axon fasciculation and growth in the developing optic pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Feb 14;114(7):1702-1707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618606114. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28137836 Free PMC article.
-
The cell adhesion molecule NrCAM is crucial for growth cone behaviour and pathfinding of retinal ganglion cell axons.Development. 2005 Aug;132(16):3609-18. doi: 10.1242/dev.01934. Epub 2005 Jul 20. Development. 2005. PMID: 16033798
-
Ganglion cell axon pathfinding in the retina and optic nerve.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Feb;15(1):125-36. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.09.006. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15036215 Review.
-
Signaling - transcription interactions in mouse retinal ganglion cells early axon pathfinding -a literature review.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2023 May 17;3:1180142. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2023.1180142. eCollection 2023. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38983012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DSCAM is differentially patterned along the optic axon pathway in the developing Xenopus visual system and guides axon termination at the target.Neural Dev. 2022 Apr 15;17(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13064-022-00161-9. Neural Dev. 2022. PMID: 35422013 Free PMC article.
-
Robo2 is required for Slit-mediated intraretinal axon guidance.Dev Biol. 2009 Nov 15;335(2):418-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.09.034. Epub 2009 Sep 25. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19782674 Free PMC article.
-
Dystroglycan Maintains Inner Limiting Membrane Integrity to Coordinate Retinal Development.J Neurosci. 2017 Aug 30;37(35):8559-8574. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0946-17.2017. Epub 2017 Jul 31. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28760865 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal ganglion cell repopulation for vision restoration in optic neuropathy: a roadmap from the RReSTORe Consortium.Mol Neurodegener. 2023 Sep 21;18(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00655-y. Mol Neurodegener. 2023. PMID: 37735444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pax6 modulates intra-retinal axon guidance and fasciculation of retinal ganglion cells during retinogenesis.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 30;10(1):16075. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72828-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32999322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avci HX, Zelina P, Thelen K, Pollerberg GE. Role of cell adhesion molecule DM-GRASP in growth and orientation of retinal ganglion cell axons. Dev Biol. 2004;271:291–305. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri AM, Broccoli V, Bovolenta P, Alfano G, Marchitiello A, Mocchetti C, Crippa L, Bulfone A, Marigo V, Ballabio A, Banfi S. Vax2 inactivation in mouse determines alteration of the eye dorsal-ventral axis, misrouting of the optic fibres and eye coloboma. Development. 2002;129:805–813. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch U, Kirchhoff F, Schachner M. Immunohistological localization of the adhesion molecules L1, N-CAM, and MAG in the developing and adult optic nerve of mice. J Comp Neurol. 1989;284:451–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

