Cholinesterase inhibitors affect brain potentials in amnestic mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 17320833
- PMCID: PMC1933386
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.120
Cholinesterase inhibitors affect brain potentials in amnestic mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
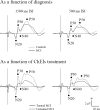
Amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is an isolated episodic memory disorder that has a high likelihood of progressing to Alzheimer's disease. Auditory sensory cortical responses (P50, N100) have been shown to be increased in amplitude in MCI compared to older controls. We tested whether (1) cortical potentials to other sensory modalities (somatosensory and visual) were also affected in MCI and (2) cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs), one of the therapies used in this disorder, modulated sensory cortical potentials in MCI. Somatosensory cortical potentials to median nerve stimulation and visual cortical potentials to reversing checkerboard stimulation were recorded from 15 older controls and 15 amnestic MCI subjects (single domain). Results were analyzed as a function of diagnosis (Control, MCI) and ChEIs treatment (Treated MCI, Untreated MCI). Somatosensory and visual potentials did not differ significantly in amplitude in MCI subjects compared to controls. When ChEIs use was considered, somatosensory potentials (N20, P50) but not visual potentials (N70, P100, N150) were of larger amplitude in untreated MCI subjects compared to treated MCI subjects. Three individual MCI subjects showed increased N20 amplitude while off ChEIs compared to while on ChEIs. An enhancement of N20 somatosensory cortical activity occurs in amnestic single-domain MCI and is sensitive to modulation by ChEIs.
Figures


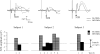
Similar articles
-
Auditory cortical activity in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: relationship to subtype and conversion to dementia.Brain. 2007 Mar;130(Pt 3):740-52. doi: 10.1093/brain/awl375. Epub 2007 Feb 9. Brain. 2007. PMID: 17293359
-
Efficacy of cognitive rehabilitation in patients with mild cognitive impairment treated with cholinesterase inhibitors.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007 Apr;22(4):356-60. doi: 10.1002/gps.1681. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17117398 Clinical Trial.
-
Auditory event-related potentials during target detection are abnormal in mild cognitive impairment.Clin Neurophysiol. 2002 Jan;113(1):151-61. doi: 10.1016/s1388-2457(01)00713-1. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11801437 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Cholinesterase Inhibitors for Mild Cognitive Impairment:A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019 Aug 12;71(2):513-523. doi: 10.3233/JAD-190546. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 31424411
-
Cholinesterase inhibitors and beyond.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2009 Apr;6(2):86-96. doi: 10.2174/156720509787602861. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2009. PMID: 19355843 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural features underlying high-accuracy classification of amnestic mild cognitive impairment using multi-sensory-evoked potentials.Geroscience. 2025 Jul 22. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01799-z. Online ahead of print. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 40696071
-
The impact of AD drug treatments on event-related potentials as markers of disease conversion.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2013 Sep;10(7):732-41. doi: 10.2174/15672050113109990148. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2013. PMID: 23905997 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive event-related potentials: biomarkers of synaptic dysfunction across the stages of Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;26 Suppl 3(0 3):215-28. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-0047. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011. PMID: 21971462 Free PMC article.
-
Musical hallucinations treated with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.Front Psychiatry. 2015 Apr 7;6:46. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00046. eCollection 2015. Front Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25904872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allison T. Scalp and cortical recordings of initial somatosensory cortex activity to median nerve stimulation in man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;388:671–678. - PubMed
-
- Bell-McGinty S, Lopez OL, Meltzer CC, Scanlon JM, Whyte EM, Dekosky ST, Becker JT. Differential cortical atrophy in subgroups of mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:1393–1397. - PubMed
-
- Celesia GG, Daly RF. Effects of aging on visual evoked responses. Arch Neurol. 1977;34:403–407. - PubMed
-
- Davis KL, Mohs RC, Marin D, Purohit DP, Perl DP, Lantz M, Austin G, Haroutunian V. Cholinergic markers in elderly patients with early signs of Alzheimer disease. J Am Med Assoc. 1999;281:1401–1406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

