The neurobehavioral benefit conferred by a single systemic administration of 8-OH-DPAT after brain trauma is confined to a narrow therapeutic window
- PMID: 17321680
- PMCID: PMC1876743
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.02.006
The neurobehavioral benefit conferred by a single systemic administration of 8-OH-DPAT after brain trauma is confined to a narrow therapeutic window
Abstract
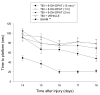
The 5-HT(1A) receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT (0.5mg/kg) enhances behavioral recovery when administered 15min after experimental traumatic brain injury (TBI). To determine if benefits are still attainable at clinically relevant times, treatment was delayed 1 and 2h post-TBI and motor/cognitive performance was compared to early (i.e., 15min) administration. No differences were observed among the vehicle and 8-OH-DPAT groups treated at 1 and 2h, but all three were significantly impaired versus early 8-OH-DPAT. The data suggest that an early and narrow critical period exists for the behavioral recovery afforded by a single 8-OH-DPAT treatment paradigm. The critical window corresponds to the well documented TBI-induced glutamate increase, suggesting that 8-OH-DPAT may be conferring neuroprotection by attenuating this acute deleterious surge.
Figures

References
-
- Alessandri B, Tsuchida E, Bullock RM. The neuroprotective effect of a new serotonin receptor agonist, BAY X3702, upon focal ischemic brain damage caused by acute subdural hematoma in the rat. Brain Res. 1999;845:232–235. - PubMed
-
- Andrade R. Electrophysiology of 5-HT1A receptors in the rat hippocampus and cortex. Drug Dev Res. 1992;26:275–286.
-
- Bullock R, Zauner A, Myseros JS, Marmarou A, Woodward JJ, Young HF. Evidence of prolonged release of excitatory amino acids in severe human head trauma. Relationship to clinical events. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1995;765:290–297. - PubMed
-
- Calcagno E, Carli M, Invernizzi W. The 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT prevents prefrontal glutamate and serotonin release in response to blockade of cortical NMDA receptors. J Neurochem. 2006;96:853–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

