The atypical cadherin flamingo regulates synaptogenesis and helps prevent axonal and synaptic degeneration in Drosophila
- PMID: 17321750
- PMCID: PMC1885973
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2007.01.007
The atypical cadherin flamingo regulates synaptogenesis and helps prevent axonal and synaptic degeneration in Drosophila
Abstract
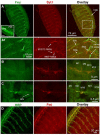
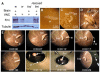
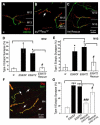
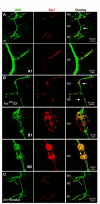
The formation of synaptic connections with target cells and maintenance of axons are highly regulated and crucial for neuronal function. The atypical cadherin and G-protein-coupled receptor Flamingo and its orthologs in amphibians and mammals have been shown to regulate cell polarity, dendritic and axonal growth, and neural tube closure. However, the role of Flamingo in synapse formation and function and in axonal health remains poorly understood. Here we show that fmi mutations cause a significant increase in the number of ectopic synapses on muscles and result in the formation of novel en passant synapses along axons, and unique presynaptic varicosities, including active zones, within axons. The fmi mutations also cause defective synaptic responses in a small subset of muscles, an age-dependent loss of muscle innervation and a drastic degeneration of axons in 3rd instar larvae without an apparent loss of neurons. Neuronal expression of Flamingo rescues all of these synaptic and axonal defects and larval lethality. Based on these observations, we propose that Flamingo is required in neurons for synaptic target selection, synaptogenesis, the survival of axons and synapses, and adult viability. These findings shed new light on a possible role for Flamingo in progressive neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures

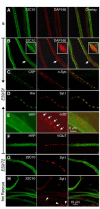
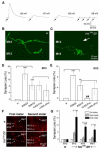
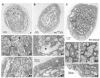
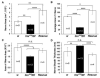
References
-
- Aberle H, Haghighi AP, Fetter RD, McCabe BD, Magalhaes TR, Goodman CS. wishful thinking encodes a BMP type II receptor that regulates synaptic growth in Drosophila. Neuron. 2002;33:545–558. - PubMed
-
- Ackley BD, Jin Y. Genetic analysis of synaptic target recognition and assembly. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:540–547. - PubMed
-
- Ahmari SE, Buchanan J, Smith SJ. Assembly of presynaptic active zones from cytoplasmic transport packets. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:445–451. - PubMed
-
- Atwood HL, Govind CK, Wu CF. Differential ultrastructure of synaptic terminals on ventral longitudinal abdominal muscles in Drosophila larvae. J Neurobiol. 1993;24:1008–1024. - PubMed
-
- Bao H, Daniels RW, Macleod GT, Charlton MP, Atwood HL, Zhang B. AP180 maintains the distribution of synaptic and vesicle proteins in the nerve terminal and indirectly regulates the efficacy of Ca2+-triggered exocytosis. J Neurophysiol. 2005;94:1888–1903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

