Approaching a complete repository of sequence-verified protein-encoding clones for Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 17322287
- PMCID: PMC1832101
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.6037607
Approaching a complete repository of sequence-verified protein-encoding clones for Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
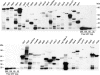
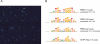
The availability of an annotated genome sequence for the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has made possible the proteome-scale study of protein function and protein-protein interactions. These studies rely on availability of cloned open reading frame (ORF) collections that can be used for cell-free or cell-based protein expression. Several yeast ORF collections are available, but their use and data interpretation can be hindered by reliance on now out-of-date annotations, the inflexible presence of N- or C-terminal tags, and/or the unknown presence of mutations introduced during the cloning process. High-throughput biochemical and genetic analyses would benefit from a "gold standard" (fully sequence-verified, high-quality) ORF collection, which allows for high confidence in and reproducibility of experimental results. Here, we describe Yeast FLEXGene, a S. cerevisiae protein-coding clone collection that covers over 5000 predicted protein-coding sequences. The clone set covers 87% of the current S. cerevisiae genome annotation and includes full sequencing of each ORF insert. Availability of this collection makes possible a wide variety of studies from purified proteins to mutation suppression analysis, which should contribute to a global understanding of yeast protein function.
Figures


References
-
- Bateman A., Coin L., Durbin R., Finn R.D., Hollich V., Griffiths-Jones S., Khanna A., Marshall M., Moxon S., Sonnhammer E.L., Coin L., Durbin R., Finn R.D., Hollich V., Griffiths-Jones S., Khanna A., Marshall M., Moxon S., Sonnhammer E.L., Durbin R., Finn R.D., Hollich V., Griffiths-Jones S., Khanna A., Marshall M., Moxon S., Sonnhammer E.L., Finn R.D., Hollich V., Griffiths-Jones S., Khanna A., Marshall M., Moxon S., Sonnhammer E.L., Hollich V., Griffiths-Jones S., Khanna A., Marshall M., Moxon S., Sonnhammer E.L., Griffiths-Jones S., Khanna A., Marshall M., Moxon S., Sonnhammer E.L., Khanna A., Marshall M., Moxon S., Sonnhammer E.L., Marshall M., Moxon S., Sonnhammer E.L., Moxon S., Sonnhammer E.L., Sonnhammer E.L., et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:D138–D141. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger M.F., Bulyk M.L., Bulyk M.L. Protein binding microarrays (PBMs) for the rapid, high-throughput characterization of the sequence specificities of DNA binding proteins. In: Bina M., editor. Gene mapping, discovery, and expression. The Humana Press, Inc.; Totowa, NJ: 2006. pp. 245–260. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bulyk M.L., Gentalen E., Lockhart D.J., Church G.M., Gentalen E., Lockhart D.J., Church G.M., Lockhart D.J., Church G.M., Church G.M. Quantifying DNA-protein interactions by double-stranded DNA arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999;17:573. - PubMed
-
- Butcher R.A., Bhullar B.S., Perlstein E.O., Marsischky G., LaBaer J., Schreiber S.L., Bhullar B.S., Perlstein E.O., Marsischky G., LaBaer J., Schreiber S.L., Perlstein E.O., Marsischky G., LaBaer J., Schreiber S.L., Marsischky G., LaBaer J., Schreiber S.L., LaBaer J., Schreiber S.L., Schreiber S.L. Microarray-based method for monitoring yeast overexpression strains reveals small-molecule targets in TOR pathway. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006;2:103–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
